Figure 5. Single suspended microvascular endothelial cells form multi-cellular structures.
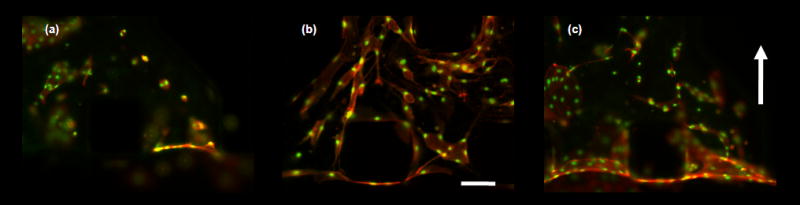
Fixed samples of microvascular endothelial cells encapsulated in collagen gels cultured for 4 days. Scale bar shown represents 125 μm. Cell were stimulated with angiogenic factors or switch to interstitial flow after 24 hours after cell seeding. (a) – (c) Micrographs of fixed samples stained for actin cytoskeleton (orange) and nucleus (green). (a) – (b) Images show the effect of biochemical stimuli. (a) cell cultured in complete EGM-2MV medium, (b) complete EGM-2MV medium supplemented with VEGF/bFGF/PMA cocktail (all at 50 ng ml−1 final concentration). Results showed a drastic difference in EC morphology and extent of multi-cellular structures organization. Control sample form EC rings that are mostly isolated from each other, while EC cultured with potent pro-angiogenic factors organize to form cellular cords. (c) Interstitial flow (flow direction indicated by arrow bottom to top), with complete medium EGM-2MV. ECs form multi-cellular structures and monolayer at gel/medium interface.
