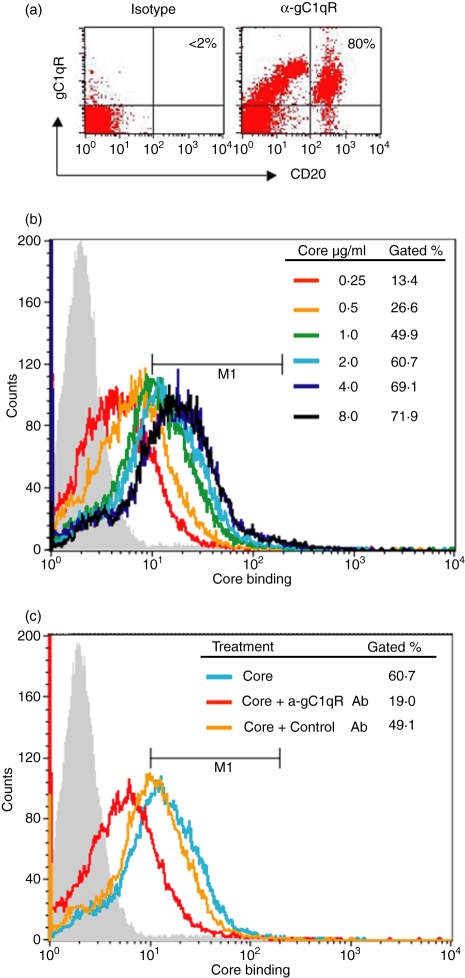
Figure 1.
HCV core protein specifically binds to gC1qR displayed on the cell surface of human B lymphocytes. (a) gC1qR expression on human B lymphocytes. A total of 1 × 106 PBMC were incubated with 1 μg/ml of anti-gC1qR or an isotype control Ab followed by 1 μg/ml of PE–anti-mouse-Ig conjugate. The cells were then double-stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-anti-CD20 Ab. The percentage of gC1qR+ cells in the CD20+ cell population is shown in the right upper corner of the dot blot. (b) Dose-dependent core binding on B lymphocytes. Magnetic antibody cell sorting (MACS)-purified B cells were incubated with escalating concentrations of HCV core protein at 37º for 2 hr and core binding on the surface of B cells was analysed by flow cytometry as described in Materials and Methods. Data were displayed as overlying histograms and the percentages of cells positive for core binding as gated based on the isotype control (grey filled area, < 2%) were shown. The histogram shifted from left to right (increasing fluorescence intensity) as the core protein increased from lower to higher concentrations until saturation. (c) HCV core binds to B lymphocytes through gC1qR. MACS-purified B cells were incubated with 2 μg/ml of HCV core protein in the presence or absence of anti-gC1qR or control antibody at 37º for 2 hr and core binding on the surface of B cells was analysed as above. Data were displayed as overlying histograms and the percentages of cells positive for core binding as gated based on the isotype control (grey filled area, < 2%) were shown.