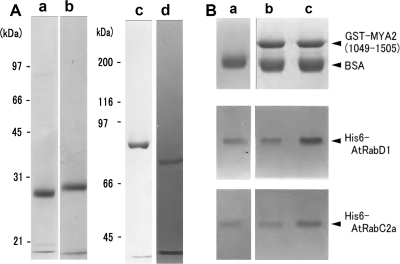
Fig. 2.
Recombinant proteins (A) and in vitro binding assay (B). (A) SDS-PAGE of His6-AtRabD1 (a), His6-AtRabC2a (b), MYA2 tail 1, aa1049-aa1505, fused with GST (c), and MYA2 tail 2, aa1049-aa1450, fused with GST (d). The molecular masses (kDa) of standard proteins in SDS-PAGE of (a), (b), (c) and (d) are indicated on the left of lanes (a) and (c), respectively. (B) In vitro binding assay using MYA2 tail 1. (a) Pellets with control beads without the adsorption of GST-MYA2 tail 1 in the presence of GTP. (b) Pellets with MYA2 tail 1 coated beads in the absence of GTP. (c) Pellets with MYA2 tail 1 coated beads in the presence of GTP. Each bead was mixed with His6-AtRabD1 or His6-AtRabC2a. After centrifugation, the pellets were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Upper, middle, and lower panels, MYA2 tail 1, His6-AtRabD1, and His6-AtRabC2a in the pellet, respectively. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was added to the mixture for preventing the non-specific binding of AtRab proteins to beads.