Fig. 4. Transamidation reactions to form Gln-tRNAGln (A) and Asn-tRNAAsn (B).
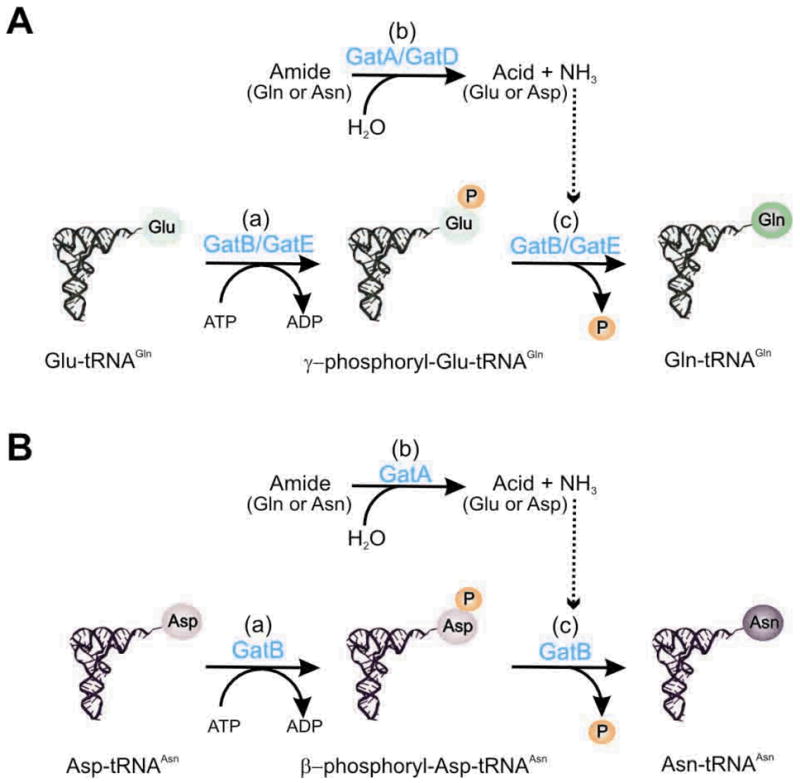
GatCAB and GatDE use the same mechanism to catalyze the tRNA-dependent transamidation. It consists of three sub-reactions: (a) the activation of the amide acceptor (tRNA bound Glu or Asp) at the expense of ATP hydrolysis, forming γ-phosphoryl-Glu-tRNAGln or possibly β-phophoryl-Asp-tRNAAsn as reaction intermediate. (b) The hydrolysis of an amide donor Gln or Asn to form enzyme captivated ammonia. (c) The transfer of sequestered ammonia to the activated intermediate to form the final product Gln-tRNAGln or Asn-tRNAAsn.
