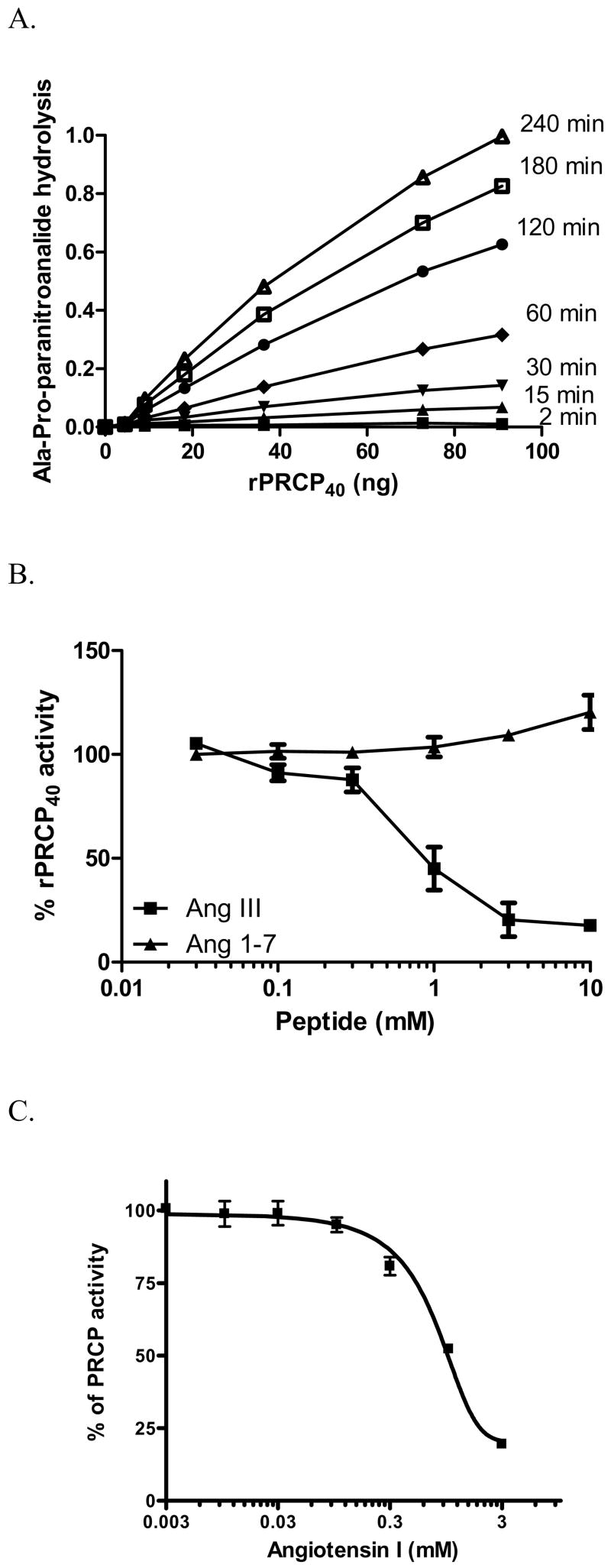
Figure 2.
Enzymatic analysis of rPRCP40. Panel A. Time course and enzyme dependency of rPRCP40 on paranitroanalide generation. The indicated concentration of rPRCP40 was incubated with 1.8 mM Ala-Pro-paranitroanalide (APpNA) in 0.01 M Na-acetate, 0.07 M KH2PO4/K2HPO4 buffer pH 5.8 at 37 °C for 2 (▪), 15 (▴), 30 (▾), 60 (●), 120 (^), 180 (□), and 240 (Δ) minutes and the amount of generated paranitroanalide expressed as OD was assessed for each rPRCP40 concentration. Panel B. Substrate inhibition of rPRCP40. The amount of paranitroanalide formed in the presence of rPRCP40 was determined by incubating each well with 1 mM Ala-Pro-paranitroanalide in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of angiotensin III (●) or angiotensin 1–7 (▪). Panel C. effect of angiotensin I (AngI) on rPRCP40. rPRCP40 was incubated with various concentrations of Ang I in the presence of rPRCP40 substrate, Ala-Pro-paranitroanalide (APpNA). Hydrolysis of APpNA was monitored at 405 nm for 3 hours. The results presented are the mean ± SEM of three separate experiments and are expressed as % rPRCP40 activity.