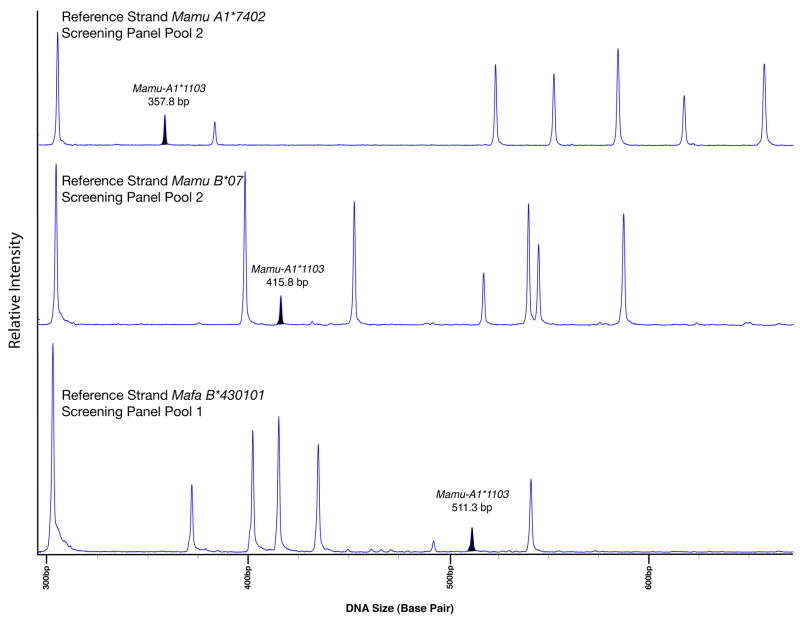
Figure 2. Use of three reference strands to vary heteroduplex migration rates for improved genotyping accuracy.
The heteroduplexes formed when screening panel sequences are hybridized with a reference strand exhibit characteristic electrophoretic mobilities. Instances in which these heteroduplexes co-migrate make genotyping more difficult. To improve genotyping resolution and overcome genotyping errors and ambiguities, the screening panel clones were hybridized to each of three distinct reference strands: Mamu-A1*7402, Mamu-B*07, and Mafa-B*430101. This example illustrates the variation in migration rate for screening panel sequence Mamu-A1*1103 when heteroduplexed with Mamu-A1*7402 (357.8 bp), Mamu-B*07 (415.8 bp), and Mafa-B*430101 (511.3 bp). The prominent peak at 304 bp is the Mamu-B*07 reference strand homoduplex.