Figure 1. Salmonella-induced intestinal inflammation is attenuated in Hfe-/- mice.
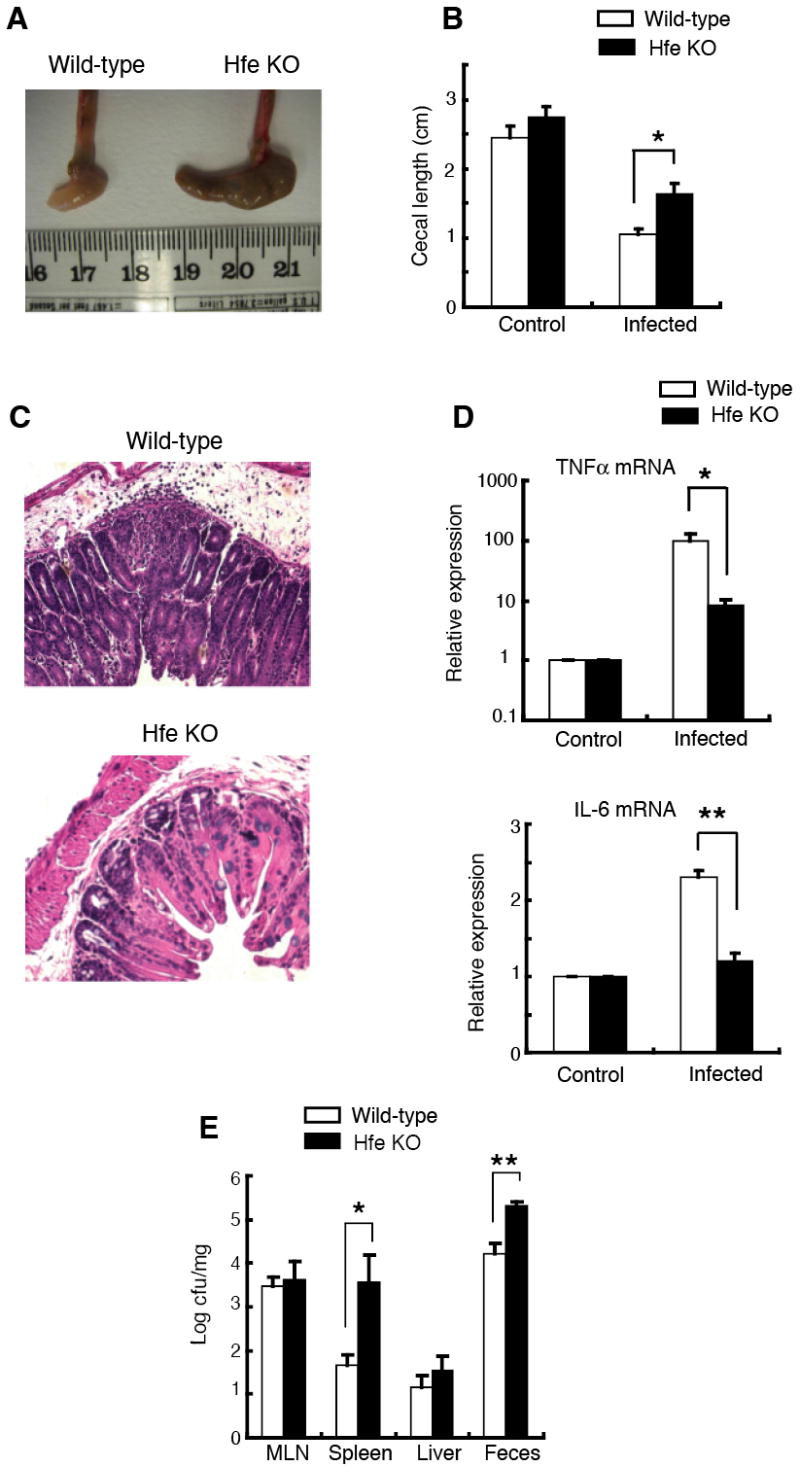
(A) Gross appearance of ceca from wild-type and Hfe knock-out (KO) mice 48 h after infection with Salmonella.
(B) Cecal lengths of wild-type and Hfe-deficient mice 48 h after infection with Salmonella. Ceca from control and infected mice were excised and the maximum length of the organ was recorded. N = 3 (control), N = 6 (infected). *p = 0.019.
(C) Cecal histopathology in wild-type and Hfe knock-out mice 48 h after infection with Salmonella (nominal magnification, 100X).
(D) Cecal TNFα and IL-6 mRNA levels in wild-type and Hfe-/- mice. Total cecal RNA from wild-type and Hfe-/- mice were subjected to quantitative RT-PCR analysis with primers specific for TNFα and IL-6. The mRNA levels of each cytokine were normalized to the housekeeping 36B4 transcript and expressed relative to control. N = 3 (control), N = 6 (infected). *p = 0.008, **p = 0.002.
(E) Numbers of Salmonella recovered from mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), spleen, liver and stool of wild-type and Hfe-deficient mice 48 h after infection. N = 9. *p = 0.039, **p = 0.044.
