Figure 5.
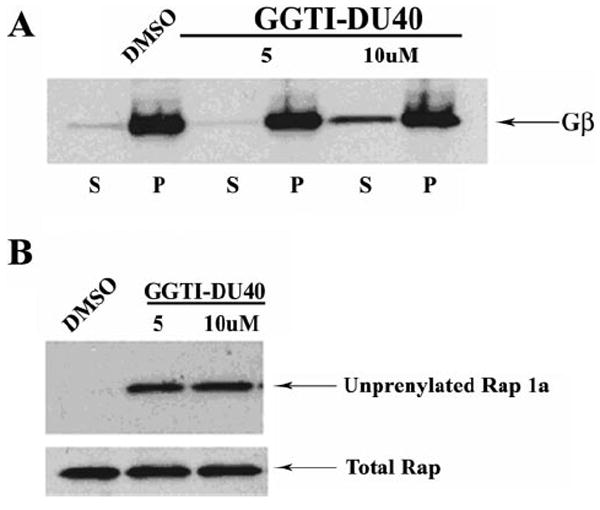
Effects of GGTI-DU40 treatment on isoprenylation of Gβγ and Rap1 in TM cells. (A) Impact of GGTI-DU40 treatment on Gβγ membrane association. TM cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of drug, lysed, and separated into soluble and insoluble fractions (100,000g pellet). Soluble (S) and insoluble (P) fractions were monitored for changes in the levels of cytosolic versus membrane-associated forms of Gβγ by immunoblot analysis. Accumulation of Gβγ in the soluble fractions of the drug-treated (10 μM) samples was observed, indicating impaired membrane targeting because of altered isoprenylation. (B) Impact of GGTI-DU40 treatment on Rap1 processing. Accumulation of unprenylated Rap1a in the drug-treated TM cells was assessed using an antibody that selectively recognizes unprenylated Rap1. Total Rap1 levels are shown for comparison and were found to be the same between control and drug-treated samples.
