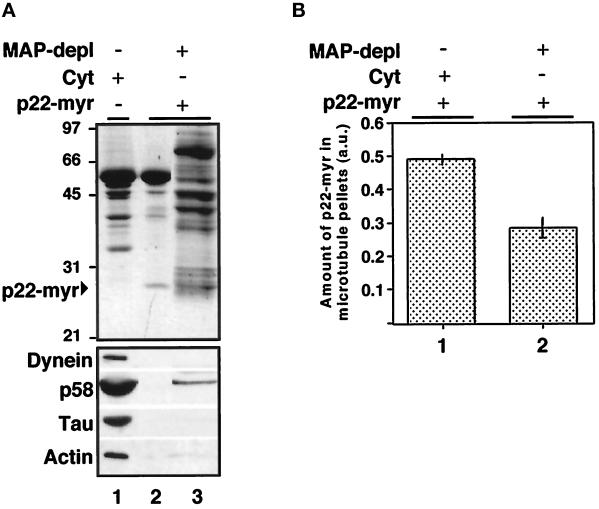
Figure 10.
MAPs and motor proteins that are removed from cytosol by microtubule affinity depletion are not necessary for the binding of p22 to microtubules. (A) A microtubule cosedimentation assay was performed in the presence of cytosol and microtubules as described above to remove MAPs and motor proteins from cytosol by microtubule pelleting (lane 1). The supernatant (MAP-depleted cytosol: MAP-depl −) was then tested for its ability to support the binding of p22-myr to extra microtubules in a second microtubule cosedimentation assay (lane 2). Equal amounts of microtubule pellets from the first and second cosedimentation assay (lanes 1 and 2) and supernatant from the second cosedimentation assay (lane 3) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining (top panel) as well as to immunoblotting with anti-dynein, anti-p58, anti-Tau (Tau 1), and anti-actin (bottom panel). (B) Equal amounts of microtubule pellets from cosedimentation assays performed in the presence of microtubules, p22-myr and cytosol (lane 1), or MAP-depleted cytosol (lane 2) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. The Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE was scanned, and the amount of p22-myr found associated with the microtubule pellet was quantitated using the NIH Image program. The bars represent the mean ± SD from three experiments.