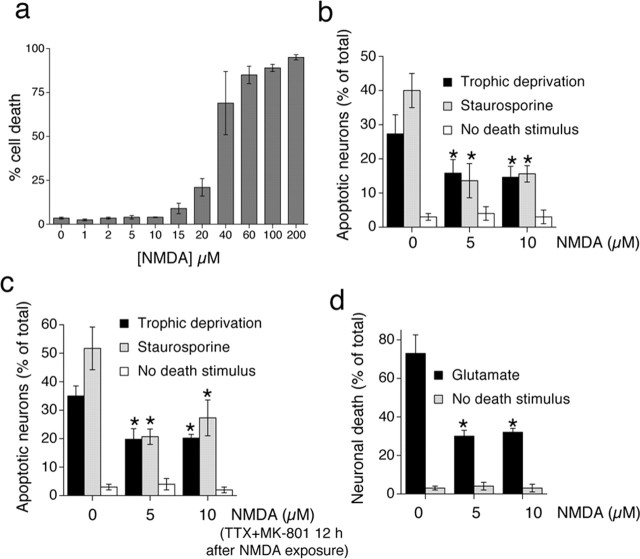
Figure 1.
Exposure to subtoxic doses of NMDA induces long-lasting neuroprotection. a, Determining the toxicity threshold of NMDA in 10 DIV hippocampal neurons. Neurons were exposed to the indicated levels of NMDA for 24 h before fixation and assessment of nuclear pyknosis. b, Subtoxic doses of NMDA protect neurons against apoptosis induced by trophic deprivation or staurosporine. Neurons were subjected to trophic deprivation (72 h) or staurosporine (36 h) in the presence of the indicated concentrations of NMDA. c, Subtoxic doses of NMDA induce long-lasting neuroprotection. Neurons were exposed to the indicated concentrations of NMDA for 12 h, after which all activity and NMDA receptors were blocked by TTX plus MK-801. Neurons then were exposed to the indicated apoptotic stimuli. d, Subtoxic doses of NMDA protect neurons against excitotoxicity. Neurons were exposed to the indicated levels of NMDA for 12 h before the toxic insult (Glutamate; 40 μm) for 1 h. Death was assessed 24 h later. In all panels, the mean ± SEM is shown of at least three independent experiments. An asterisk indicates significant neuroprotection as compared with control neurons not exposed to NMDA; p < 0.05; paired two-tailed t test.