Figure 4.
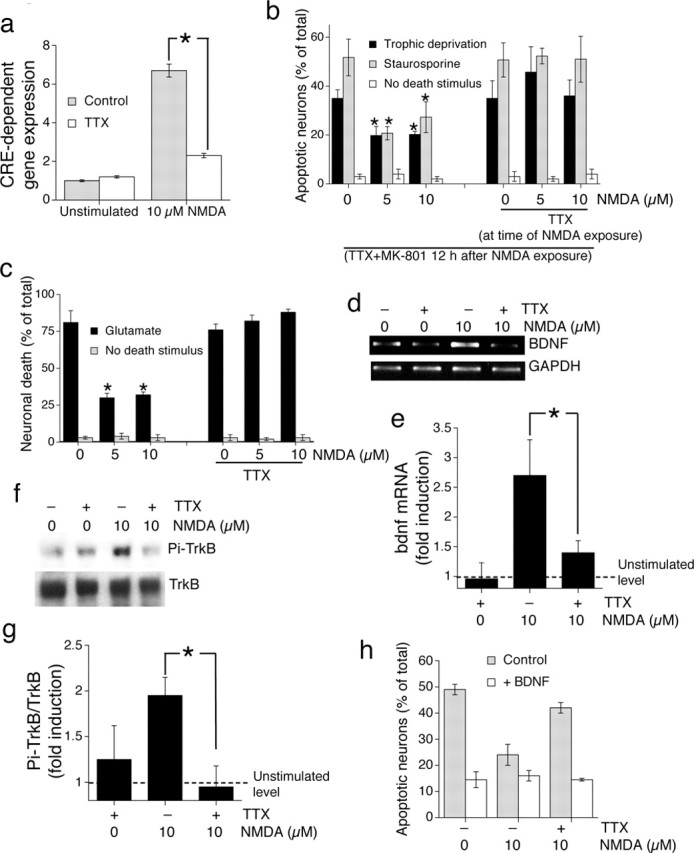
NMDApre induction of CREB-dependent neuroprotection relies on enhanced firing; chronic low-level NMDA receptor activity is not sufficient. a, Activation of CRE-dependent gene expression by NMDApre is AP dependent. Neurons were transfected with CRE-firefly luciferase plus Renilla transfection control and stimulated as indicated for 6 h. ∗p < 0.05; paired two-tailed t test (n = 4). b, The long-lasting CREB-dependent phase of NMDApre-dependent neuroprotection is dependent on AP firing. Neurons were exposed to the indicated concentrations of NMDA ± TTX for 12 h, after which all activity and NMDA receptors were blocked by TTX plus MK-801. Neurons were then exposed to the indicated apoptotic stimuli. An asterisk indicates significant neuroprotection as compared with control neurons not exposed to NMDA; p < 0.05; paired two-tailed t test (n = 4). c, NMDApre-induced neuroprotection against excitotoxic insults is dependent on firing activity. Neurons were exposed to the indicated level of NMDA ± TTX for 12 h before the toxic insult (Glutamate; 40 μm) for 1 h. Death was assessed 24 h later. In all panels, the mean ± SEM is shown of at least three independent experiments. An asterisk indicates significant neuroprotection as compared with control neurons not exposed to NMDA; p < 0.05; paired two-tailed t test. d, Induction of BDNF mRNA expression by NMDApre is AP dependent. RT-PCR was performed on RNA extracts from neurons treated for 4 h as indicated. The example shown is typical of three similar experiments. e, Analysis of all three experiments performed by digital scanning of gel photographs, with BDNF band intensity normalized to GAPDH; ∗p < 0.05, paired two-tailed t test. f, g, NMDApre induces TrkB activation that is AP dependent. Neurons were stimulated as indicated for 1 h, followed by Western blot analysis of phospho-TrkB. The example shown is typical of three similar experiments, the analysis of which is shown in g. ∗p < 0.05; paired two-tailed t test. h, BDNF supplementation is sufficient to reverse the inhibitory effect of TTX on NMDApre-induced neuroprotection. Neurons were subjected to trophic deprivation (72 h) and treated as indicated in the presence or absence of BDNF (25 ng/ml).
