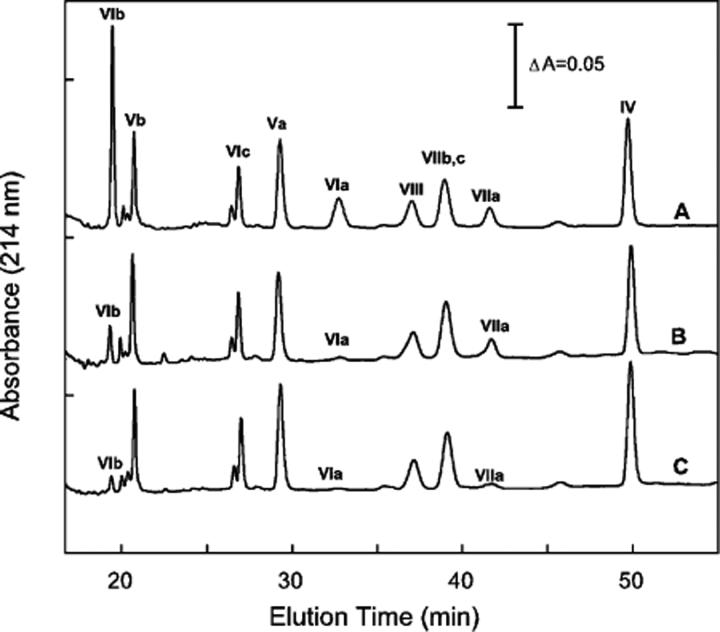
Figure 4.
Reversed-phase HPLC analysis of nuclear-encoded subunits of CcO and its pressure-generated subcomplexes. Monomeric CcO, after exposure to 3 kbar of hydrostatic pressure for 2 h, was separated by HiTrapQ anion-exchange chromatography into three distinct chromatographic species, i.e., A, B, and C in Figure 3, and the subunit content of each was determined by quantitative reversed-phase HPLC analysis (27). Nearly identical subunit compositions were obtained each time the HiTrapQ peaks were analyzed. Data are representative of more than a dozen analyses: (A) subunit content of HiTrapQ peak A, (B) subunit content of HiTrapQ peak B, and (C) subunit content of HiTrapQ peak C. For each analysis, CcO eluting in a HiTrapQ peak was pooled, acidified with 0.2% TFA, and 50−100 μg of protein injected onto the RP-HPLC column.