Figure 5.
Mutation Analysis of LH3
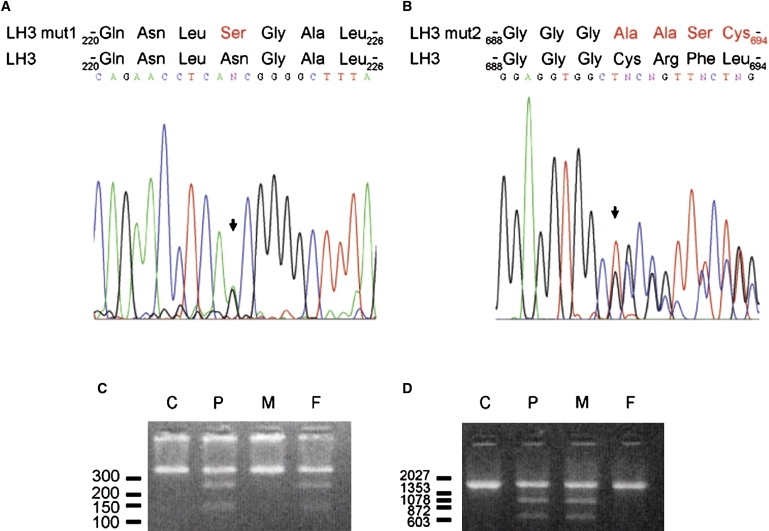
Sequence analysis of LH3 cDNA of the patient revealed a heterozygous nucleotide transition c.668A→G (arrow in [A]) generating amino acid change p.Asn223Ser in the sequence (mutation 1), and a heterozygous one nucleotide deletion c.2071 delT (arrow in [B]) causing p.Cys691AlafsX9 frameshift in the amino acid sequence (mutation 2). We used digestion of PCR amplified DNA fragment by restriction enzymes to screen the mutations in DNA of parents. We used oligonucleotides (A20 5′-aagagagagaaaagtgagaaat-3′ and A15 5′-tgtgcaacagatgccagac-3′) from introns 5 and 6 to screen mutation 1. Oligonucleotides (A7 5′-gagcagcgagagcctcctac-3′ and A1 5′-actgtctccagctcaggcaat-3′) from intron 17 and 3′ downstream region of PLOD3 were employed for identification of mutation 2. Digestion of genomic DNA fragment by BbvCI (NEB) (C) or NarI (NEB) (D) and analysis of the fragments by agarose gel after ethidium bromide staining indicated that the mutation 1 was inherited from the father and mutation 2 was inherited from the mother. DNA markers are indicated (bp). C, control; P, patient; M, mother; F, father.
