Figure 6.
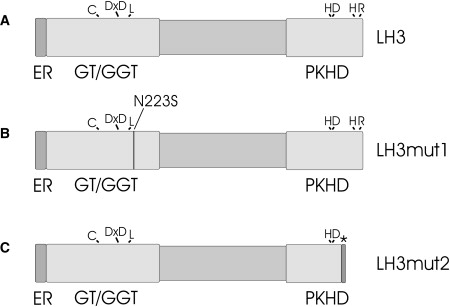
Domain Representation of Human LH3
(A) Putative N-terminal ER signal sequence (ER, amino acids 1–24) is followed by glycosyltransferase (GT/GGT) domain (25–280), which is responsible for GT/GGT activities and has structural similarities with glycosyltransferases.3 Lysyl hydroxylase/prolyl 4-hydroxylase (PKHD) domain (565–738) shares homology with 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases and includes a 2-oxoglutarate and ironII-dependent oxygenase domain. Domain borders are approximated by sequence comparisons. Amino acids that are important for activity are indicated in the corresponding domain. DxD motif is a typical domain of glycosyltransferases and is also crucial for LH3 activity. LH3mut1 (B) is a protein produced by mutation 1 (c.668A→G) resulting p.Asn223Ser amino acid substitution. LH3mut2 (C) is a result of mutation 2 (c.2071 delT), in which one nucleotide deletion causes a frameshift and premature stop-codon formation (p.Cys691AlafsX9). The size of a LH3mut2 protein is 698 amino acids. The asterisk represents the last eight amino acids of LH3mut2 differing from LH3 as a result of frameshift and premature stop codon formation.
