Figure 4.
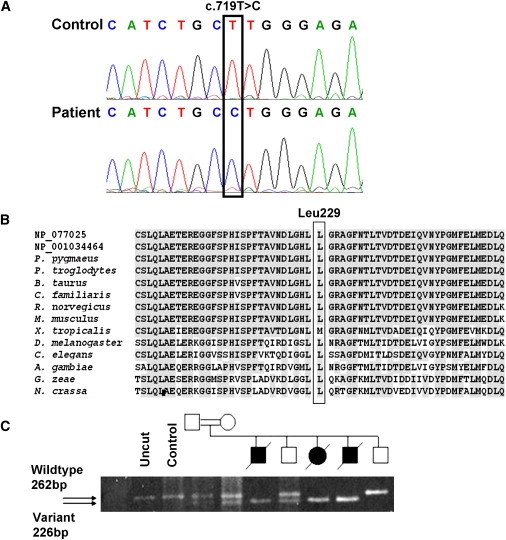
Mutation Analysis of C20orf7
Nomenclature is based on NM_024120.3.
(A) Sequencing chromatograms showing the c.719T→C mutation in the proband's genomic DNA, which predicts a Leucine-to-Proline substitution at codon 229.
(B) Amino acid alignment of C20orf7 orthologs shows that Leu229 and the surrounding region are highly conserved (gray shading). The alignment of the mutated region was generated with ClustalW via sequences obtained from BLASTp with both human transcripts: NP_077025 and NP_001034464. Sequences are from Pongo pygmaeus (orangutan, accession number CAH90789), Pan troglodytes (chimpanzee, XP_514521), Bos taurus (bovine, XP_600505), Canis familiaris (dog, XP_534340), Rattus norvegicus (rat, XP_215857), Mus musculus (mouse, NP_081369), Xenopus tropicalis (frog, NP_001016398), Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly, AAL29045), A. gambiae str. PEST (mosquito, EAA05526), Gibberella zeae PH-1 (fungus, EAA70416), Neurospora crassa (fungus, CAD11326).
(C) BstNI restriction-enzyme-based analysis of the mutation in genomic DNA from family members shows that only DNA from affected individuals is homozygous for the BstNI site introduced by the mutation. The parents and one unaffected sibling are heterozygous, and one unaffected sib is homozygous for the wild-type allele.
