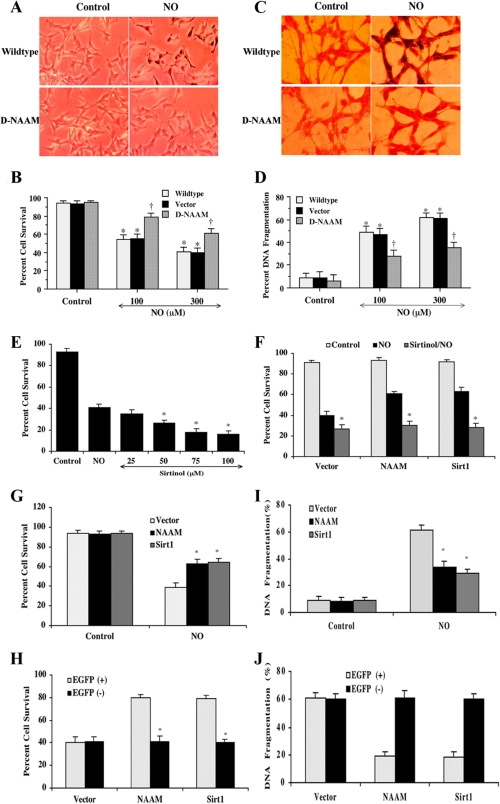
FIGURE 7.
D-NAAM expression protects human neuronal cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death. A-D, SH-SY5Y cells transfected with control vector or D-NAAM or nontransfected cells were exposed for 24 h to 100 or 300 μm NOC-9 and analyzed for cell death using trypan blue exclusion (A and B) or assayed for apoptotic cell death using deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay (C and D). For quantification of cell death and DNA fragmentation, on average, 200 cells were counted in triplicate samples (B and D). † denotes p value <0.01, and asterisks denote statistically nonsignificant difference between nontransfected and vector-transfected cells. E and F, control SH-SY5Y cells (E) or cells expressing EGFP control vector, EGFP-D-NAAM or EGFP-Sirt1 (F) were treated with the indicated concentrations of sirtinol (E) or 50 μm sirtinol (F) 1 h prior to exposure to 300 μm NOC-9 and cell survival was determined 24 h later as in B. G-J, SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with EGFP control vector, EGFP-D-NAAM, or EGFP-Sirt1; cell survival in response to 300 μm NOC-9 was analyzed as in B (G), and apoptotic cell death was analyzed as in D (I). Alternatively, EGFP positive and negative cells were analyzed separately (H and J). The asterisks denote p value <0.01.