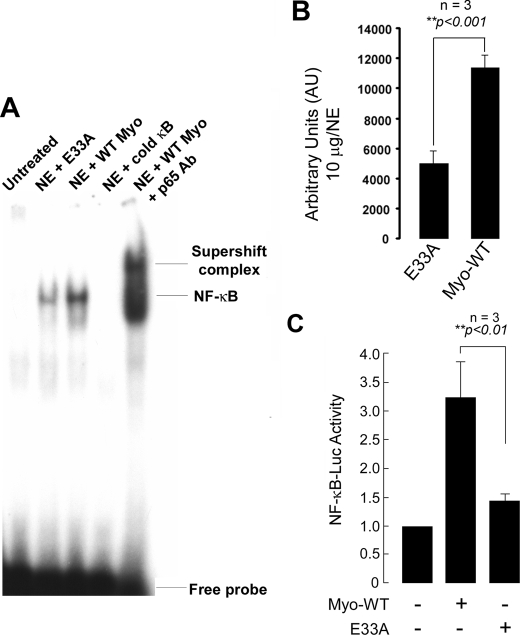
FIGURE 9.
NF-κB activation in wild type and E33A myotrophin-treated neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. A, nuclear protein was extracted from control (no stimulation), wild type (WT), and E33A myotrophin-treated neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. Binding reactions were performed with NF-κB oligonucleotide labeled with [32P]dATP. The complex formation was competed with100-fold molar excess of unlabeled NF-κB oligonucleotide. The complex formation was confirmed by supershift analysis using p65 antibody. NE, nuclear extract. B, quantification of electrophoretic mobility shift assay using ImageJ software. The values obtained from three independent experiments are expressed as arbitrary units for 10 μg/nuclear extract (p < 0.001). C, primary neonatal rat myocytes were transfected with 2× NF-κB-Luc reporter plasmid (1 μg/well) and treated with 40 nm myotrophin (wild type E33A) for 24 h or left untreated. The cells were also transfected with empty vector. After harvesting the cells, Luciferase activity was determined and normalized to the protein content of each extract. Luciferase activity expressed by cells transfected with empty vector was given an arbitrary value of 1. The results are presented as the means ± S.E. and represent three individual experiments.