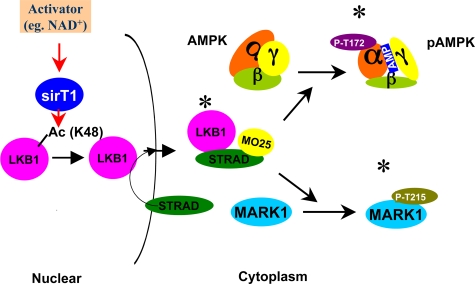
FIGURE 5.
Proposed mechanism of LKB1 activation by SIRT1. Activation of LKB1 and LKB1 target molecules by SIRT1, proposed mechanism. Factors that activate SIRT1 lead to deacetylation of one (Lys-48) or more key lysine residues on LKB1. This in turn enhances LKB1 binding to STRAD and MO25, which increases its kinase activity, and leads to the phosphorylation and activation of AMPK, MARK1, and possibly other LKB1 targets. The scheme assumes that LKB1 acetylation by SIRT1 occurs in the nucleus and that this facilitates LKB1 movement to the cytoplasm by binding to STRAD. Not shown is that the activation of LKB1 by STRAD also leads to LKB1 phosphorylation at Ser-428 and Thr-336 (see text). (* = activated enzyme.)