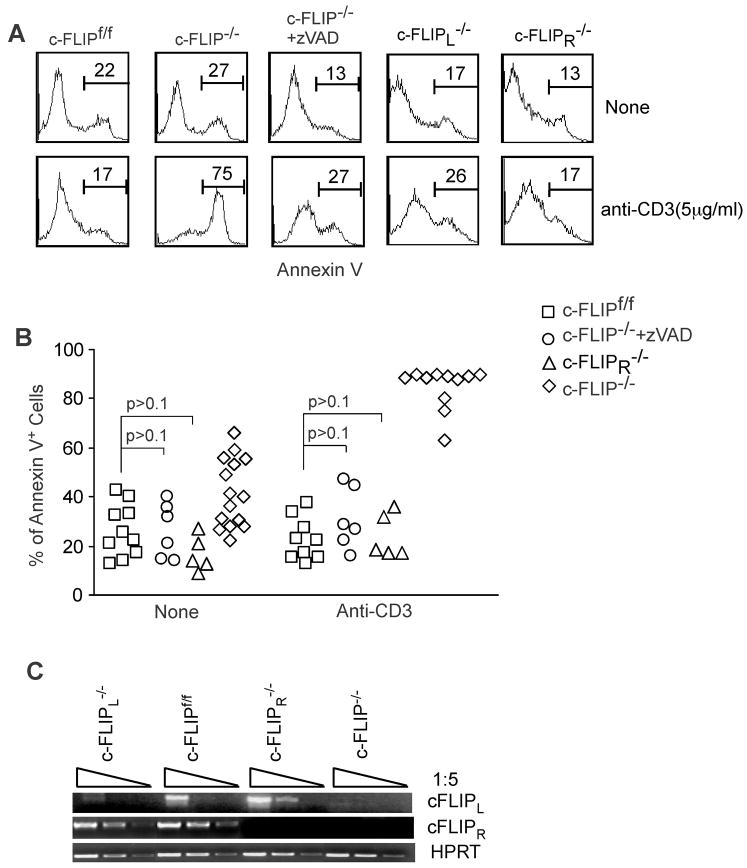
Figure 2. Both c-FLIPL and c-FLIPR are anti-apoptotic in TCR-induced death of c-FLIP−/− T cells.
(A) Expression of c-FLIPL or c-FLIPR in c-FLIP-deficient T cells or addition of the caspase inhibitor zVAD rescues the defective survival of c-FLIP-deficient T cells. Total splenocytes and LN cells from c-FLIPf/f, c-FLIPf/fER-Cre (c-FLIP−/−), c-FLIPf/fER-Cre.c-FLIPR BAC Tg (c-FLIPL−/−), and c-FLIPf/fER-Cre.c-FLIPL BAC Tg (c-FLIPR−/−) were cultured for three days with 4OH-tamoxifen. Live cells were purified and recultured under different conditions for another 24 hours. 10 μM zVAD was used in the reculture period. The apoptotic rate of CD4+ T cells was determined by Annexin V staining. (B) Cumulative data on CD4+ T cell apoptosis from different treatments. Data are from five independent experiments as shown in (A). Each dot represents one mouse. (C) Expression of c-FLIPL or c-FLIPR in T cells lacking c-FLIP, c-FLIPL or c-FLIPR Three days after 4OH-tamoxifen culture as described in (A), live cells were purified and subjected to RT-PCR analysis. HPRT serves as a loading control.