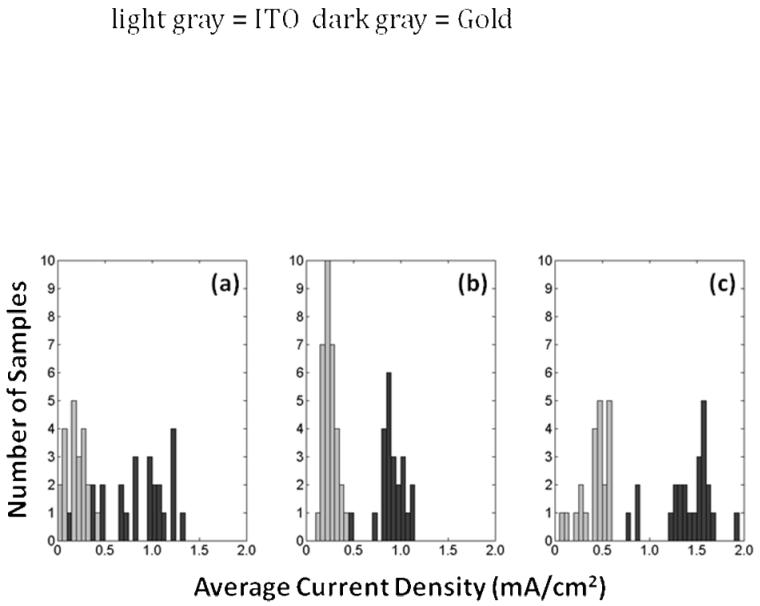
Figure 2. Histograms of the Average Current Density (charge passed/(area*time)) in Electrochemical Syntheses.
Syntheses on ITO (light gray) and gold (dark gray) are shown for Cl-doped films (a), ToS-doped films (b), and PSS-doped films (c). Gold electrode substrates consistently resulted in higher current density and thus higher deposition rates, which may impact the yield or efficiency of the amount of material polymerized for a given charge passed. The higher variability in the current density during Cl-doped film synthesis may relate to high variability of film thicknesses observed. All syntheses were performed under the same conditions: 0.1 M concentration of pyrrole and dopant ions, room temperature, neutral pH, and aqueous solvent (distilled, de-ionized water).