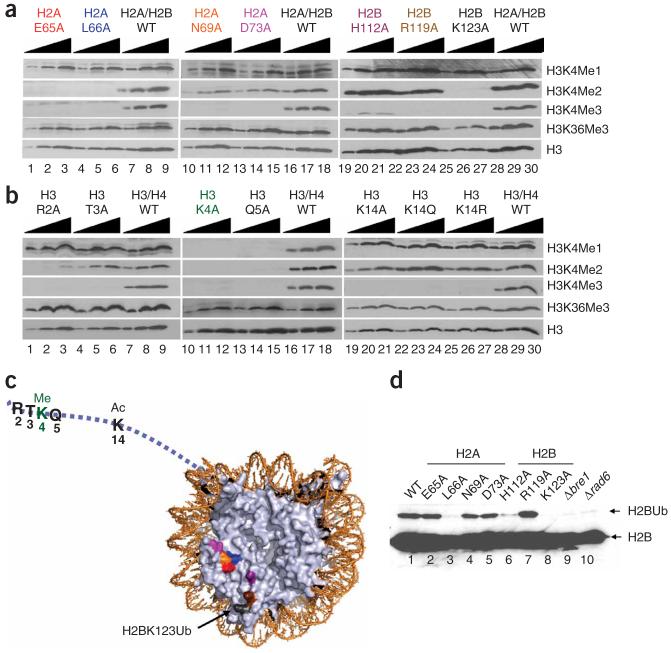
Figure 6.
Identification of a nucleosomal patch regulating the H3K4 methylation pattern. (a,b) Titration analyses of histone mutants identified as defective in proper H3K4 methylation. Titration analysis was performed to confirm the positive hits obtained from GPS analysis. Extracts were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by western blot analysis, and testing for the presence of monomethylated lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4Me1), dimethylated lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4Me2) and trimethylated lysine 4 of histone H3 (H3K4Me3). As a positive control, extracts from the strain carrying a plasmid containing wild-type histone (either HTA1 and HTB1 or HHT2 and HHF2) were loaded onto each individual gel. (c) The locations of residues required for normal levels of H3K4 methylation were mapped onto nucleosomes of the crystal structure (PDB 1ID3)60. Ac, acetylation; Ub, monoubiquitination. (d) Identification of histone amino acid residues required for H2B monoubiquitination. Extracts from H2A and H2B mutants identified as defective in Lys4 methylation were tested for the presence of H2B monoubiquitination.