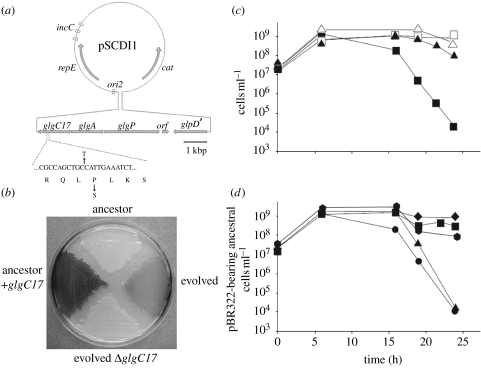
Figure 4.
Genetic basis of SCDI in ABM E. coli. (a) Map of the pSCDI1 plasmid. The genes glgC, glgA and glgP encode the enzymes ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase, respectively. orf denotes an open reading frame that encodes a putative membrane protein with no significant homology to any known protein (data not shown). glpD′ is the truncated 3′ portion of the gene for the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. ori2, repE and incC are the cis-elements that are necessary for the mini-F type plasmid replication. cat, chloramphenicol acetyl transferase. The partial sequence below the glgC gene shows the base pair substitution leading to the Pro to Ser change in GlgC17. (b) Iodine staining of the pBR322-carrying ABM derivatives ancestor, evolved and evolved ΔglgC17, and of the ancestor carrying the glgC17-bearing multicopy plasmid pMLM141 (ancestor+glgC17). (c) glgC17 protects from SCDI. Plating efficiency of naive cells containing pMLM141 (triangles) or the pBR322 vector (squares) in mixed cultures with evolved cells (solid symbols) or in single cultures (empty symbols). (d) glgC17 is responsible for SCDI. Plating efficiency of pBR322-containing ancestral Ara+ cells was monitored in single cultures (diamonds) or in mixed cultures with Ara− ancestral cells containing pBR322 (squares); evolved, evolved ΔglgC17 cells containing pBR322 (hexagons); Ara− ancestral cells containing pMLM141 (triangles); evolved cells containing pBR322 (circles).