Figure 5.
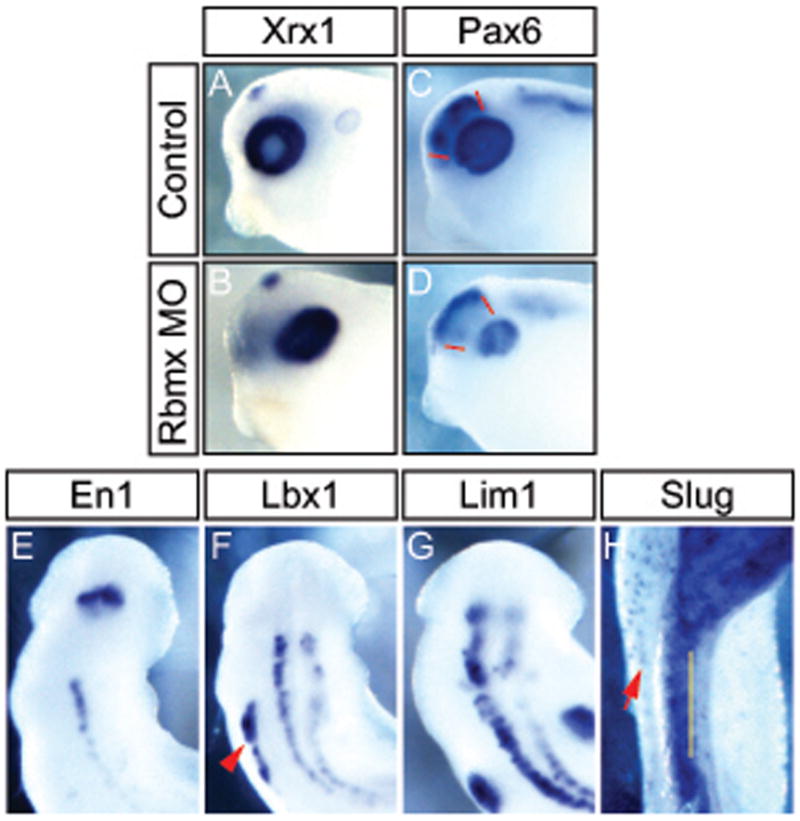
Rbmx is required for normal eye development and neuronal differentiation. Embryos injected unilaterally with Rbmx MO and cultured to stage 31 (A–D), stage 28 (E–F), or stage 35 (H). (A,B) In situ hybridization for Xrx1. (C,D) In situ hybridization for Pax6; red lines indicate Pax6 expression domain in normal forebrain (C), which is absent in the Rbmx MO injected side (D). (E–H) dorsal view of head and anterior trunk of Rbmx morphants. Injected side is to the right. (E–H) In situ hybridization using antisense probe for En1 (E), Lbx1 (F), Lim1 (G), and Slug (H). Red arrowhead in (F) indicates Lbx1 expression in hypaxial muscle on the uninjected side. Yellow line in (H) indicates the midline and red arrow indicates melanocytes on the uninjected side. Notably Slug expression is absent in the neural tube and trunk on the injected side.
