Figure 2. Conventional RT-PCR amplification of CD158e/KIR3DL1 and CD158k/KIR3DL2 in erythrodermic skin samples.
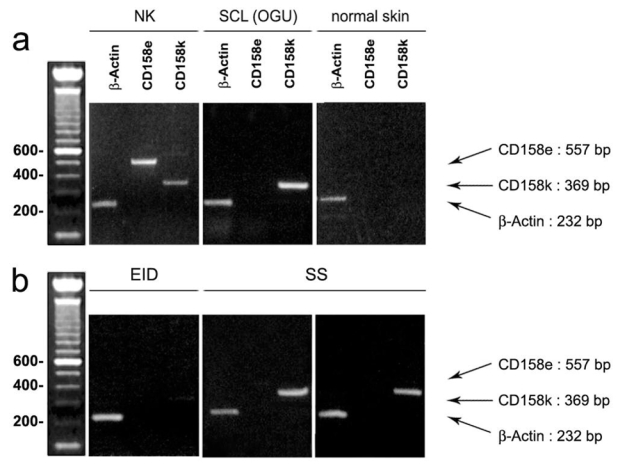
(a) Controls. In natural killer lymphocytes from a healthy donor, used as a positive control, both CD158e/KIR3DL1 and CD158k/KIR3DL2 transcripts are found (left), whereas in the Sézary cell line OGU, only CD158k/KIR3DL2 appears to be positive (middle). By contrast, in normal skin used as a negative control, both CD158e and CD 158k RT-PCR are negative (right), (b) Skin biopsies from patients with erythroderma.. In the skin sample from the EID group, neither CD158e/KIR3DL1 nor CD158k/KIR3DL2 mRNA expression is detected (left). By contrast, in the two SS samples (middle and right), a significant expression of CD158k/KIR3DL2 is found, with a bright distinctive band at the expected size, whereas CD158e/KIR3DL1 transcript are not detected.
