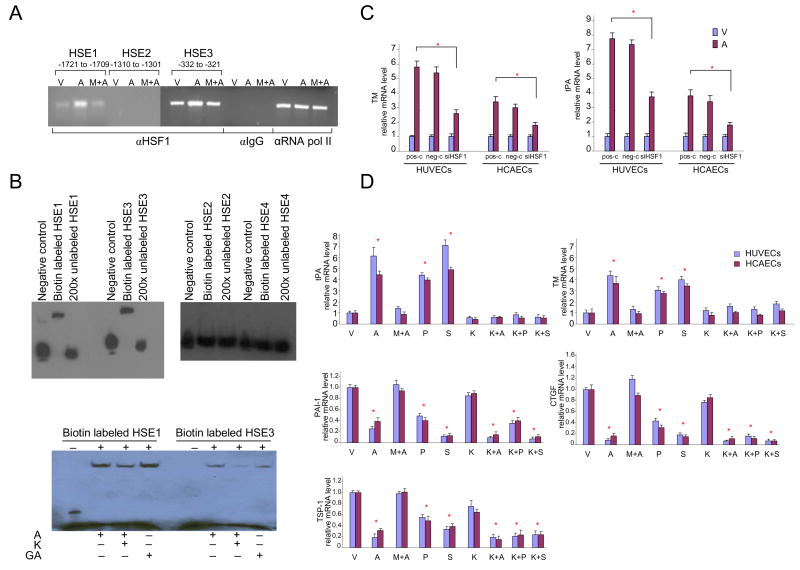
Figure 2. Statin-induced binding of HSF1 to HSE1 and HSE3 and influence of inhibition of HSF1 binding on pleiotropic statin effects.
A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay showing binding of HSF1 to HSE1 and HSE3.
HUVECs were treated with vehicle (V), atorvastatin (A), or pre-treated with mevalonate for 30 minutes before being treated with atorvastatin (M+A) for 6 hours and subjected to ChIP analysis. Immunoprecipitated DNA was isolated and amplified by PCR.
B) EMSA analysis confirming binding of HSF1 to HSE1 and HSE3 in the TM promoter. HUVECs were treated with atorvastatin (A), geldanamycin (GA), or pre-treated with KNK437 (K) for 60 minutes before being treated with atorvastatin for 6 hours. Nuclear extracts were then subjected to EMSA analysis.
C) Knockdown of HSF1 reduces the effect of atorvastatin on endothelial expression of TM and tPA.
Knockdown of HSF1 was performed with siRNA. After 48 hours, HUVECs and HCAECs were treated with vehicle or atorvastatin for 24 hours. TM and tPA mRNAs were quantified by real-time PCR.
D) Influence of inhibition of binding of HSF1 to HSE on pleiotropic statin effects. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis of RNA from HUVECs and HCAECs treated with vehicle (V), statins (atorvastatin, A; pravastatin, P; simvastatin, S); pre-treated with mevalonate for 30 minutes before being treated with atorvastatin (M+A); KNK437 (K), or pre-treated with KNK437 for 60 minutes before being treated with statins (atorvastatin, K+A; pravastatin, K+P; simvastatin, K+S) for 24 hours.
Atorvastatin: 1×10−5M; pravastatin: 4×10−5M; simvastatin: 1×10−5M; mevalonate: 5 ×10−4; KNK437:1×10−;4.
* p < 0.05 versus vehicle.