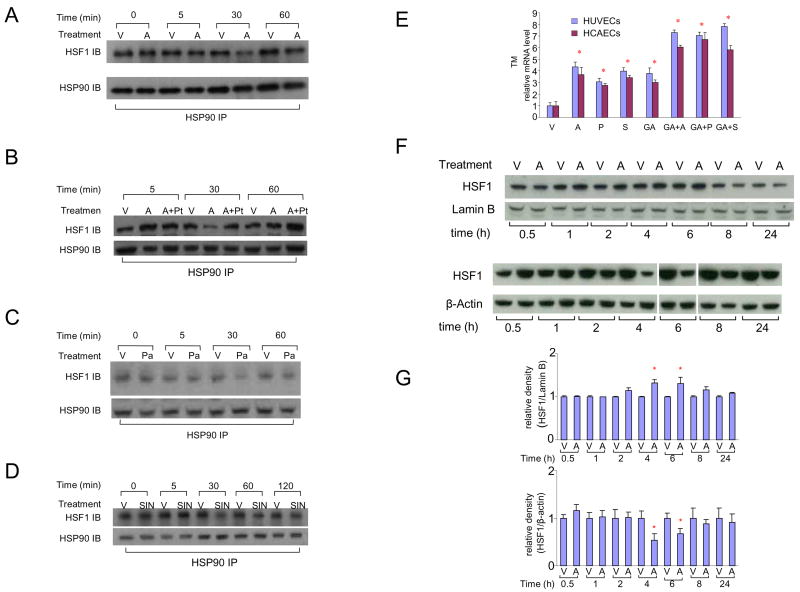
Figure 3. Atorvastatin causes NO-dependent dissociation of HSF1 from HSP90 followed by nuclear translocation of HSF1.
A) Dissociation of HSF1 from HSP90 after 30 minutes exposure of endothelial cells to atorvastatin.
HUVECs were exposed to vehicle (V) or atorvastatin (A) for 0–60 minutes and anti-HSP90 immunoprecipitated protein was analyzed by anti-HSF1 and anti-HSP90 western blot.
B) Inhibition of atorvastatin-induced HSF1-HSP90 dissociation by co-exposure to an NO scavenger.
HUVECs were treated with vehicle (V), atorvastatin (A), or pre-treated with PTIO, an NO scavenger, for 30 minutes before being treated with atorvastatin (A+Pt) for up to 60 minutes. Immunoprecipitated protein was analyzed by western blot.
C) Exposure of endothelial cells to a slow NO donor causes HSF1-HSP90 dissociation. HUVECs were treated with vehicle (V), or PAPA (Pa), a slow NO donor, for up to 60 minutes. Immunoprecipitated protein was analyzed by western blot.
D) Exposure of endothelial cells to a rapid NO donor causes HSF1-HSP90 dissociation. HUVECs were treated with vehicle (V), or SIN-1 (SIN), a rapid NO donor, for up to 120 minutes. Immunoprecipitated protein was analyzed by western blot.
E) Activation of HSF1-HSP90 dissociation upregulates TM.
TM transcript levels in HUVECs and HCAECs treated with vehicle (V), statins (atorvastatin, A; pravastatin, P; simvastatin, S); geldanamycin (GA); GA combined with statins (atorvastatin, GA+A; pravastatin, GA+P; simvastatin: GA+S) for 24 hours.
F) Increase in nuclear HSF1 content and decrease in cytoplasmic HSF1 content after exposure of endothelial cells to atorvastatin for 4–6 hours.
Total cytoplasmic (bottom) and nuclear (top) proteins were harvested from HUVECs treated with vehicle (V) or atorvastatin (A) for up to 24 hours, and analyzed by western blots.
G) Densitometric analysis of blots shown in panel F.
Atorvastatin: 1×10−5M; pravastatin: 4×10−5M; simvastatin: 1×10−5M; geldanamycin: 2μg/ml; PTIO: 1×10−4M; PAPA: 1×10−5M; SIN-1: 1×10−5M.
* p < 0.05 versus vehicle.