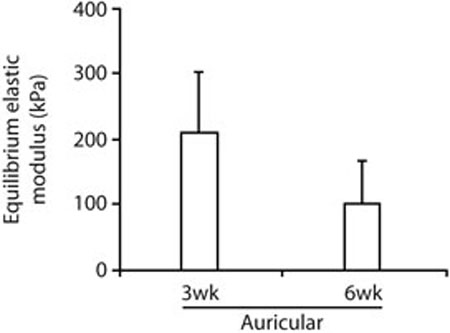
FIG. 2.
Quantitative results from biomechanical testing. Five of six auricular samples successfully completed biomechanical testing. All tissue-engineered cartilage samples generated from articular or nasal chondrocytes lacked the mechanical integrity and stiffness necessary for completion of the test. The higher equilibrium elastic modulus of auricular samples at 3 weeks than at 6 weeks was not statistically significant (p = 0.21, by unpaired t test).