Figure 3.
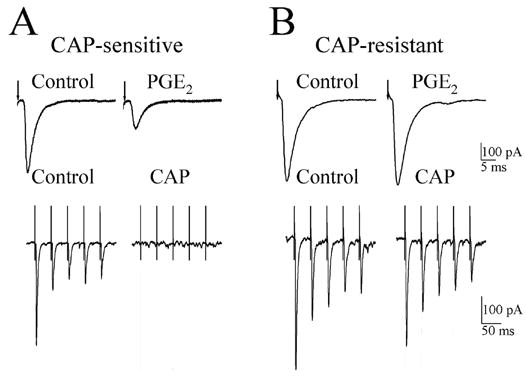
Effect of PGE2 on the amplitude of afferent evoked EPSCs (evEPSCs) recorded in capsaicin-sensitive and capsaicin-resistant second-order NTS neurons. A, top panel, 200 nM PGE2 decreased the evEPSC amplitude recorded in a capsaicin-sensitive neuron. Lower panel, shows five consecutive evEPSCs before (control) and following a 10 min superfusion with 200 nM capsaicin (CAP); note the evEPSCs were completely blocked by CAP treatment. B, top panel, PGE2 (200 nM) did not affect the evEPSC amplitude in CAP-resistant neuron. Lower panel shows a train of five evEPSCs recorded from the same neuron before (control) and 10 min after superfusion with 200 nM CAP. Each trace is an average of 10 responses. The arrows in A and B shows the time of the stimulus artifact.
