Figure 3. Phylogenetic distribution of metazoan-type cell adhesion domains and sequence-specific transcription factor families.
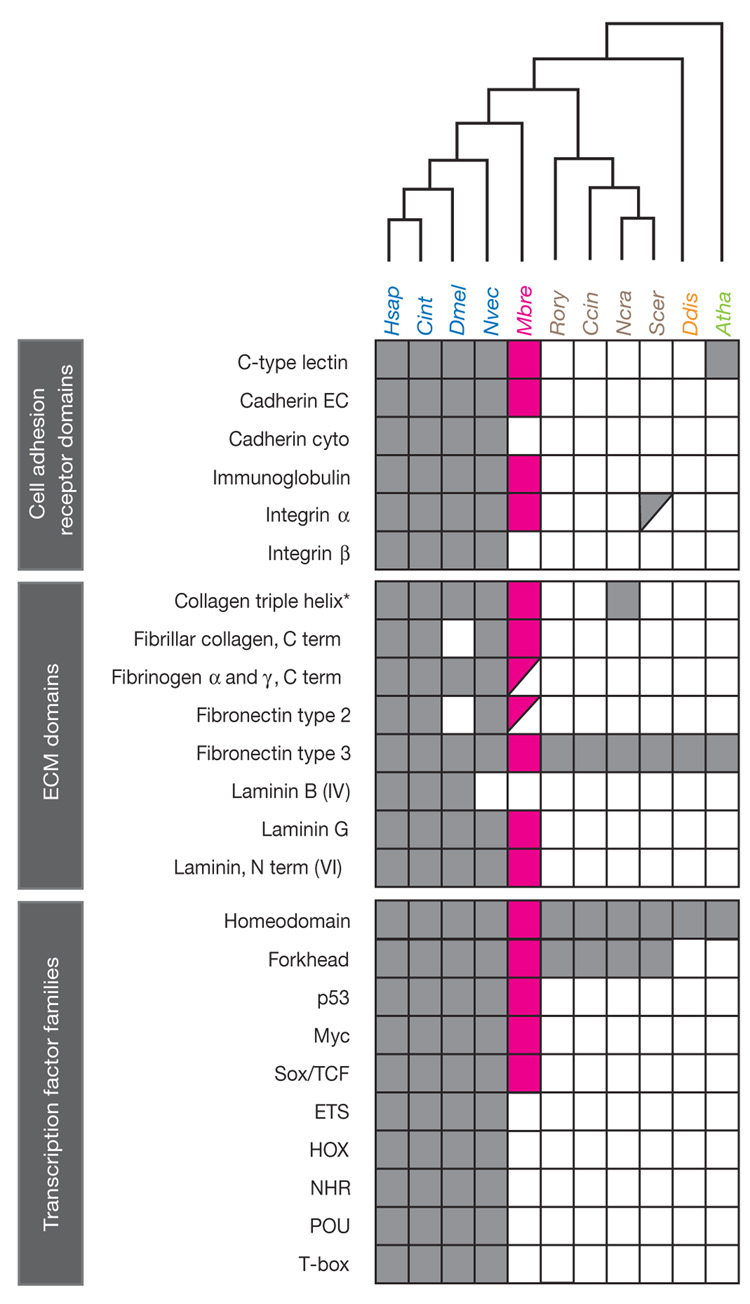
M. brevicollis possesses diverse adhesion and ECM domains previously thought to be unique to metazoans (magenta). In contrast, many metazoan sequence-specific transcription factors are absent from the M. brevicollis gene catalogue. For adhesion and ECM domains, a filled box indicates a domain identified by both SMART and Pfam37,48, a half-filled box indicates a domain identified by either SMART or Pfam, and an open box indicates a domain that is not encoded by the current set of gene models. The presence (filled box) or absence (empty box) of transcription factor families was determined by reciprocal BLAST and SMART/Pfam domain annotations (Supplementary Note 3.5). Species names follow the convention from Fig. 1. EC, extracellular domain; cyto, cytoplasmic domain; asterisk, collagen triple-helix-domains occur in the extended tandem arrays diagnostic of collagen proteins found only in metazoans and choanoflagellates.
