Fig. 3. Proposed two-state model for the allosteric behavior of RMPK.
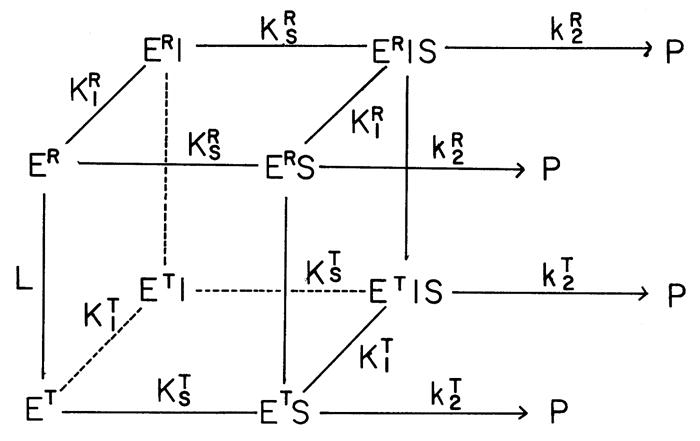
E, S, P and I are enzyme, substrate (phosphoenolpyruvate, PEP or ADP), product (pyruvate) and inhibitor (Phe), respectively. ER and ET are the two structural states. The species are interconnected with equilibrium constant, L=[ET]/[ER]; KR and KT are the ligand binding equilibrium constants associated to the ER- and ET-state, respectively, while KI and KS are the equilibrium constants associated with the binding of inhibitor Phe and substrate, respectively. kT and kR are the catalytic rates of ER and ET, respectively [16].
