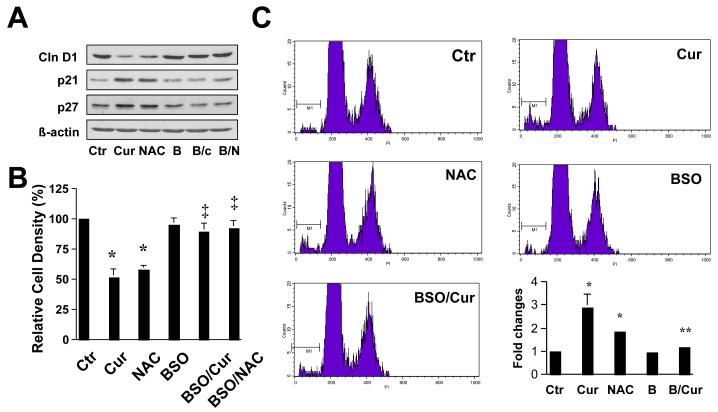
Figure 7. de novo synthesis of GSH plays a critical role in the inhibitory effect of curcumin on HSC growth.
Passaged HSC were either maintained in DMEM with 10% of FBS, or treated for 24 hr with BSO (0.25mM), or curcumin (20μM), or NAC (5mM) with or without the pre-exposure to BSO (0.25mM) for 1 hr. (A). Western blotting analyses of proteins relevant to cell growth. ß-actin was used as an invariant control for equal loading. Representatives of three independent experiments were shown; (B). Cell growth was determined by MTS assays. Values were expressed as means ± S.D (n=3). *p<0.05, versus control cells with no treatment (the 1st column on the left); ‡ p<0.05, versus cells treated with curcumin, or NAC (the 2nd or 3rd column, respectively, on the left). (C). Flow cytometric analyses of apoptosis (n=3). *p<0.05, versus control cells with no treatment (the 1st column on the left); ** p<0.05, versus cells treated with curcumin (the 2nd column on the left).