Figure 3.
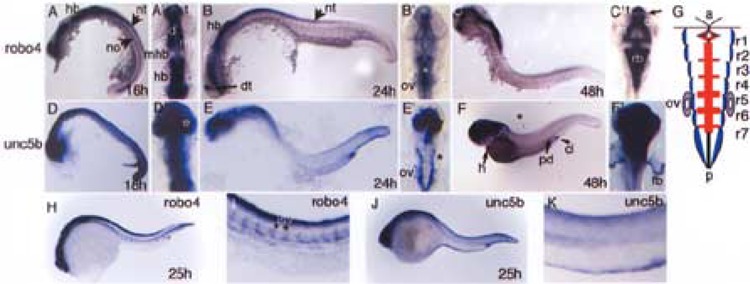
Comparisons of robo4 and unc5b brain expression patterns during zebrafish embryonic brain development. Wild-type embryos probed for robo4 and unc5b transcripts across three comparable developmental stages of brain development are shown. For each whole mount in situ, corresponding flat mount of the head region is depicted. (A), (B), and (C) show robo4 in situ embryos at 16, 24, and 48 hpf, respectively, along with (A′), (B′), and (C′) showing the corresponding flat mounts of the head region. Similarly, (D), (E), and (F) show unc5b in situ embryos at 18, 24, and 48 hpf along with their corresponding flat mounts of head region in (D′), (E′), and (F′). Asterisks in (B′) medial clusters of rhombomere cells and in (E′) unc5b expression in bilateral cluster of cells in rhombomeres. Arrows in (A) and (B) depict neural structures neural tube and notochord; arrow in (C′) shows separation of robo4 and non-robo4 expression domains in telencepha-lon. Short arrow in (F) shows cloaca and long arrows depict posterior pronephric duct region and heart. (G) A pictorial representation of blue regions (unc5b, E′), red regions (robo4, B′) in the rhombomeres (r1–r7) of a 24 hpf developing zebrafish hindbrain along with otic vesicle shown in purple to depict both transcript expression. (H–K) In situs for robo4 and unc5b genes at 25 hpf with emphasis on vascular expression in the trunk region (I, K). Abbreviations used include a: anterior, cl: cloaca, d: diencephalon, e: eye, fb: fin bud, h: heart, hb: hindbrain, isv: intersomitic vessels, m: mesencephalon, mb: midbrain, mhb: midbrain hindbrain boundary, no: notochord, nt: neural tube, ov: otic vesicle, p: posterior, pd: pronephric duct, t: telencephalon.
