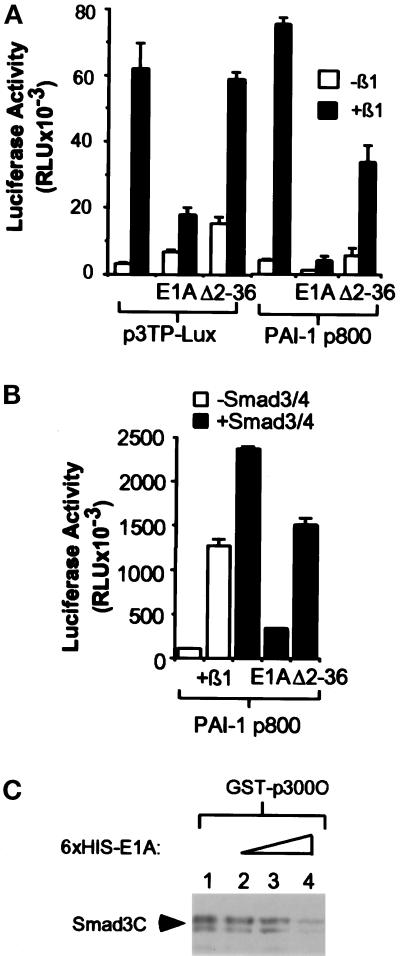
Figure 4.
E1A inhibits Smad-dependent transcriptional activation. (A) E1A, but not the p300 binding mutant E1AΔ2–36, blocks transcriptional activation of 3TP-Lux and PAI-1-Luc. HaCaT cells were cotransfected with 3 μg of 3TP-Lux or PAI-1-Luc reporter constructs and 4 μg of the indicated E1A expression constructs. The total amount of DNA was kept constant with the addition of vector control pCDNA3. TGF-β was added 12 h after transfection, and luciferase activity was measured 24 h later. Error bars represent the SD for duplicate transfections in a single experiment. “E1A” stands for wild-type E1A, and “Δ2–36” stands for E1AΔ2–36 mutant. (B) The transcriptional activation induced by Smad3/Smad4 overexpression is inhibited by E1A in a p300-dependent manner. HaCaT cells were cotransfected with 3 μg of PAI-1, 3 μg of Smad3/Smad4, and 4 μg of E1A expression constructs as indicated. The total DNA amount was kept constant with the addition of pCDNA3. After transfection and TGF-β treatment, luciferase activity was measured as above. (C) E1A can compete with Smad3 for interaction with p300. COS-overexpressed HA-tagged Smad3C (aa 199–424) was used to access the ability of Smad3 to interact with p300 in the presence of E1A. Eluted bacterial-produced 6XHis E1A was added in increasing amounts from lanes 2 to 4 to the GST-p300C pull-down reaction. After incubation at 4°C for 2 h, the bound proteins were washed three times with lysis buffer and immunoblotted with antibodies against HA.