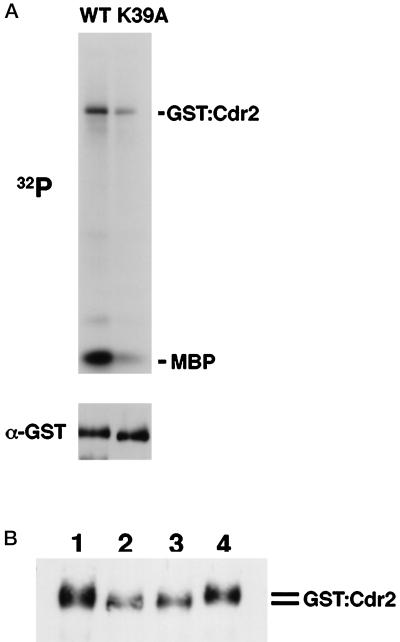
Figure 9.
GST–Cdr2 appears to undergo autophosphorylation in vivo. (A) Wild-type strain transformed with pJL205-cdr2 or pJL205-cdr2K39A was grown in the absence of thiamine, and the cell extracts were prepared. GST fusion proteins were precipitated by using GSH–Sepharose and assayed for kinase activity in the presence of myelin basic protein (MBP). Anti-GST immunoblotting shows that approximately equal amounts of GST–Cdr2 protein were used in this assay (bottom panel). (B) Phosphatase treatment causes a mobility shift of GST–Cdr2. Cell extracts of asynchronous wild-type cells carrying pJL205-cdr2 or pJL205-cdr2K39A were prepared, and GST fusion proteins were precipitated by using GSH–Sepharose and subjected to calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) treatment. Lane 1, wild-type Cdr2 with no CIAP treatment; lane 2, Cdr2K39A with no CIAP; lane 3, wild-type Cdr2 with CIAP; lane 4, wild-type Cdr2 with CIAP and phosphatase inhibitors. Western blotting with antibodies to GST is shown.