Figure 4.
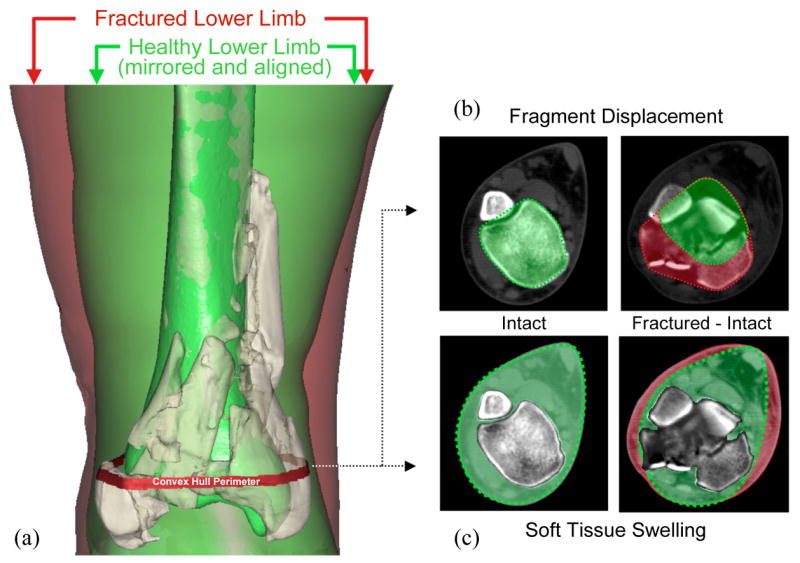
Assessment of fragment displacement and soft tissue injury began with (a) alignment of the proximal base of the fractured tibia with a mirrored image of its healthy contralateral limb. (b) In each CT slice, a convex hull (the smallest convex polygon circumscribing an object) of both the mirrored intact, and of the composite aligned intact and fractured tibias was generated. The difference in circumscribed volumes between these convex hulls was used to quantify fragment dispersion and axial mal-alignment in a single aggregate displacement metric. (c) Fracture-associated soft tissue swelling was quantified by calculating the mathematical difference in volume of non-osseous regions in the fractured and intact limbs.
