Fig. 2. Biochemical characterization of ceMTM3.
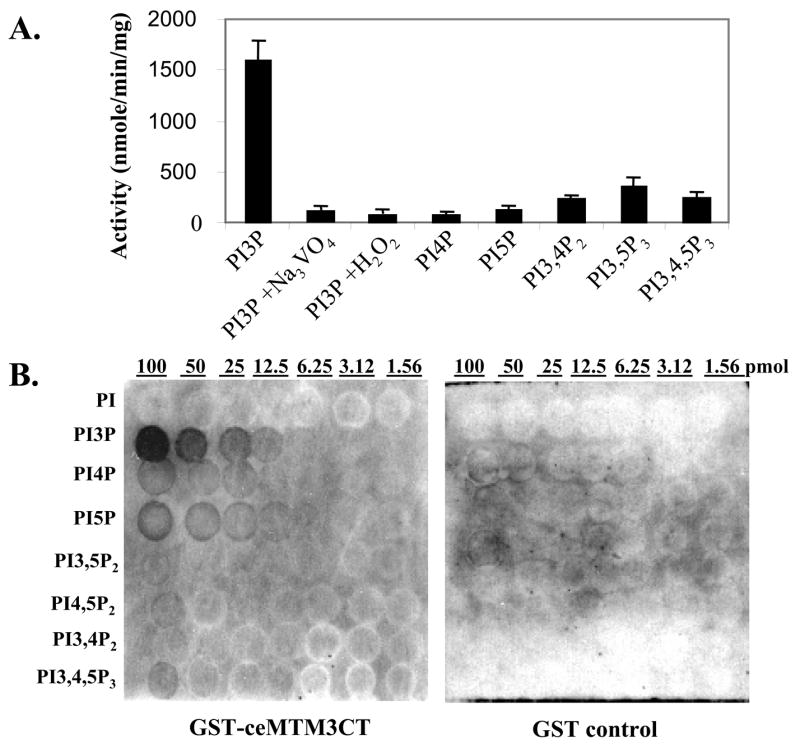
A. Substrate specificity of ceMTM3. ceMTM3 was immuno-purified from worm extracts. Phosphatase activity assays with various phosphoinositides were performed at pH 6.0 with 5 μM each of lipids (Echelon Research Lab, Salt Lake City, UT). For PI3P, assays were also performed in the presence of 1 mM sodium vanadate or 0.1 mM hydrogen peroxide. Error bars denote standard deviation (n = 3). B. Binding specificity of the FYVE domain of ceMTM3. PIP arrays (Echelon Research Lab, Salt Lake City, UT) with indicated amounts (1.56 – 100 pmol) of various phopshoinositides were probed with 0.5 μg/ml GST-ceMTM3CT or GST in a washing buffer containing 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 0.15 M NaCl, 0.1% Tween-20, and 3% fatty acid-free BSA. Bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody and HRP-conjugated secondary antibody.
