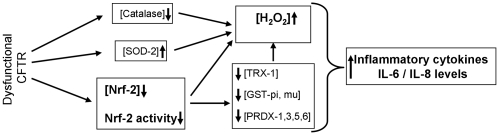
Figure 8. Schematic of the mechanism of H2O2 regulation its impact on inflammation in CF.
Our proteomic analysis of in vitro and in vivo models of CF indicate differential expression of redox proteins that regulate H2O2, predicting an increase in peroxide, which we confirmed by biochemical analysis. The mechanism involves a paradoxical decrease in Nrf-2 expression and activity caused by the loss of CFTR function in CF cells. Furthermore, we demonstrate the effect of this phenomenon on inflammation in CF.