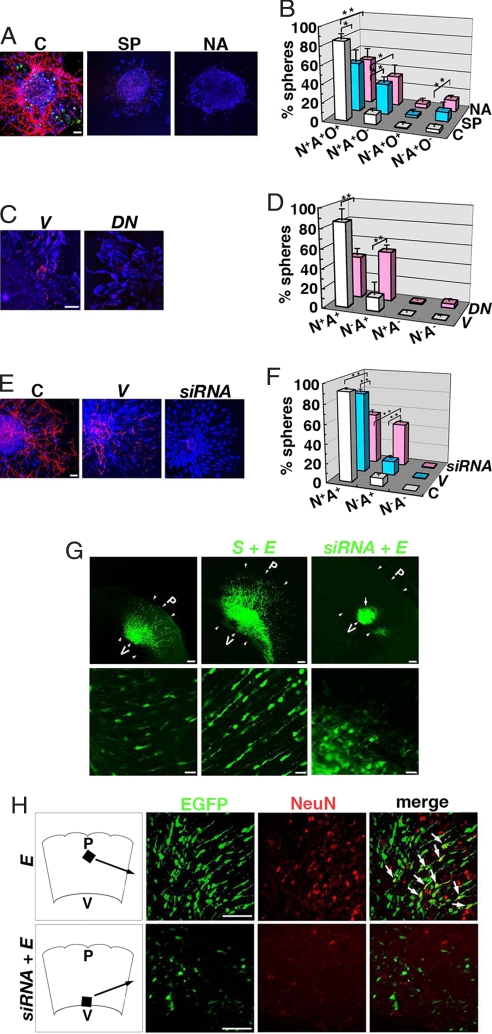
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of SIRT1 impairs neuronal differentiation. (A) Neurospheres were cultured in the absence (C) or presence of SIRT1 inhibitors (SP, splitomicin; NA, nicotinamide) and stained with anti-Tuj1 (neurons, red), anti-GFAP (astrocytes, blue), and anti-O4 (oligodendrocytes, green) antibodies. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (B) The number of neurospheres containing Tuj1+ (N), GFAP+ (A), and/or O4+ cells (O) was counted. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (C) NPCs were electroporated with control vector (V) or SIRT1H355Y (DN) and immunostained after differentiation. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (D and F) The number of spheres containing Tuj1+ (N) and/or GFAP+ (A) cells was counted. **, P < 0.01. (E) NPCs were untreated (C) or infected with lentivirus vector (V) or SIRT1-siRNA lentivirus (siRNA) and immunostained after differentiation. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (G) E14 brain was electroporated with EGFP (E), SIRT1-EGFP with EGFP (S + E), or SIRT1-siRNA with EGFP (siRNA + E) and examined at E17. Arrowheads indicate tangential thickness of the brain section. P, pia; V, ventriculus. (Scale bars: Upper, 100 μm; Lower, 20 μm.) (H) NeuN immunostaining of E17 brains. Black arrows indicate the localization of the sections. White arrows indicate EGFP+/NeuN+ cells. (Scale bars: 50 μm.)