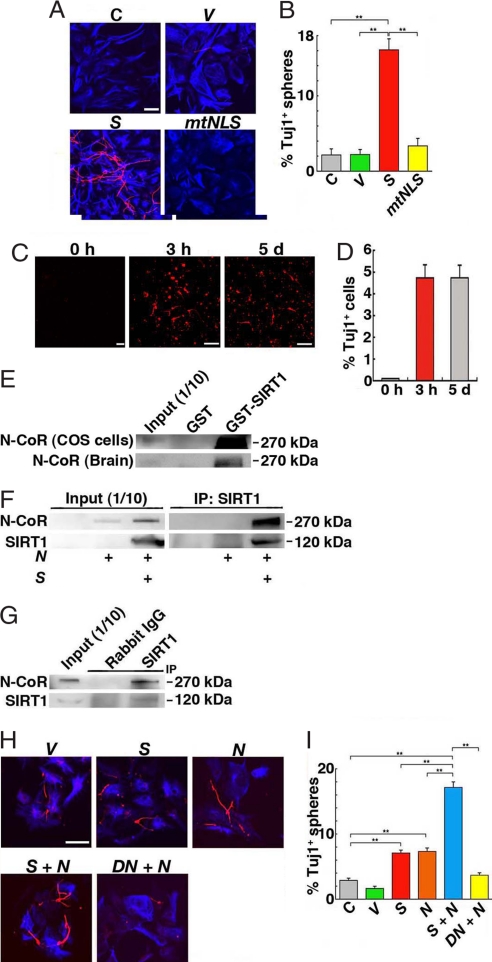
Fig. 3.
SIRT1 and N-CoR promotes neuronal differentiation. (A) NPCs were untreated (C) or transfected with vector (V), SIRT1 (S) or SIRT1mtNLS (mtNLS) and then immunostained with anti-Tuj1 (red) and anti-GFAP (blue) antibodies after differentiation. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (B) The number of spheres containing Tuj1+ cells was counted. More than 20 visual fields were counted for each experiment. **, P < 0.01. (C) NPCs were cultured in the differentiation conditions for 3 h and then cultured in MHM medium containing EGF and bFGF for 5 days (3 h). For control, NPCs were cultured in the differentiation conditions for 5 days (5 d). Cells were immunostained with an anti-Tuj1 antibody. (Scale bars: 50 μm.) (D) Tuj1+ cells were counted. (E) GST-SIRT1 binds N-CoR from COS cells and fetal brain. (F and G) Immunoprecipitation of N-CoR with anti-SIRT1 antibody. (F) N-CoR in COS cells is coimmunoprecipitated with SIRT1. (G) N-CoR from E16.5 embryonic brain cells cultured in differentiation conditions for 3 h is immunoprecipitated by anti-SIRT1 antibody. (H and I) SIRT1 and N-CoR induce neuronal differentiation. NPCs transfected with the indicated plasmids (V, control vector; S, SIRT1; N, N-CoR; DN, SIRT1H355Y) were analyzed. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (I) The number of spheres containing Tuj1+ cells was counted. **, P < 0.01.