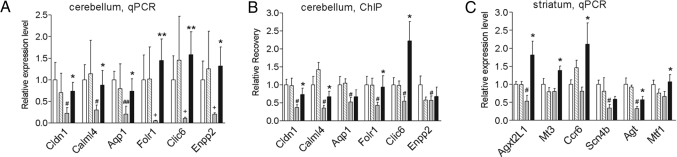
Fig. 5.
HDAC inhibitor treatment reverses mRNA abnormalities and increases acetylated H3 in association with genes down-regulated in R6/2300Q transgenic mice. Real-time PCR analysis was performed for the indicated genes on RNA samples from the cerebellum (A) or striatum (C) of vehicle- (white bars) or HDACi 4b–treated (striped bars) WT mice and vehicle- (gray bars) or HDACi 4b–treated (filled bars) R6/2300Q transgenic mice. Data are depicted as fold change of the mean expression level ± SEM (n = 4 mice per group). The relative abundance of each gene expression was normalized by using Hprt. (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-acetylated histone H3 (AcH3) and anti-histone H3 antibodies on the cerebellum of vehicle- or HDACi 4b-treated WT and R6/2300Q transgenic mice (same key as in A and C). Real-time PCR was performed with primers for the promoter region of Cldn1 and Aqp1 and the transcribed region of Calml4, Folr1, Clic6, and Enpp2. Recovery was normalized for Gapdh, and data are shown as the ratio of the recovery for AcH3 and H3 and normalized for vehicle-treated WT mice ± SEM. Student's t tests were used to determine significant differences in gene expression or recovery levels. The effect of drug treatment on expression of the sodium channel, type IV-β gene (Scn4b) in the striatum of HD mice did not reach significance. # denotes significantly different values between R6/2300Q transgenic and WT mice at P < 0.05, with + denoting P < 0.08; * denotes significantly different values between HDACi 4b- and vehicle-treated R6/2300Q mice at P < 0.05 and ** at P < 0.01.