Figure 3.
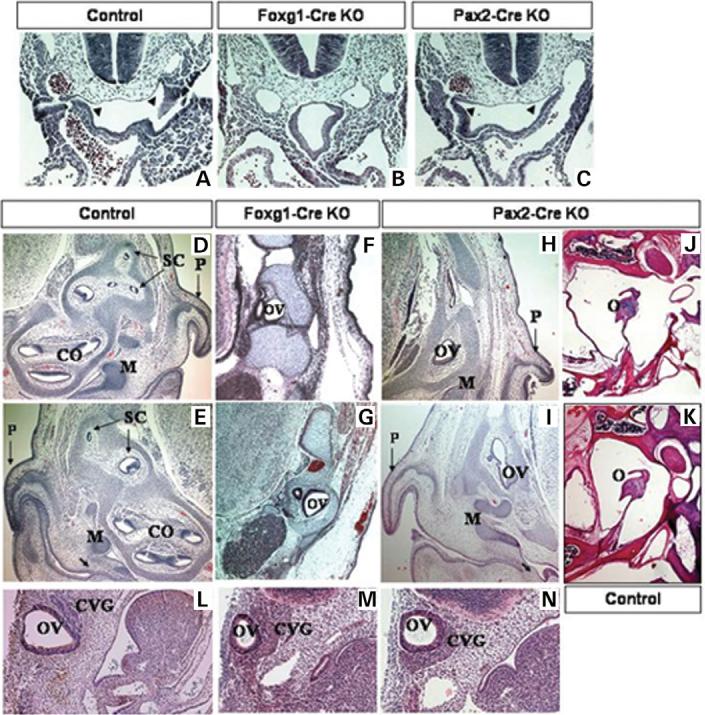
E10.5 transverse histological sections of control (A), Foxg1-KO (B) and Pax2-Cre KO (C) embryos. The invaginating pharyngeal endoderm in control (A) and Pax2-Cre KO (C) embryos is denoted with arrowheads. E17.5 transverse histological sections of control (D and E), Foxg1-Cre KO conditional mutants (F and G) and Pax2-Cre KO (H and I) embryos. Note the presence of the nascent tympanum in controls (E) and Pax2-Cre KOs (I), denoted by an arrow, and the middle ear bones (M), as opposed to Foxg1-Cre KOs (F,G). Horizontal histological sections of adult conditional mutant Pax2-Cre KO (J) and control (K) mice show the presence of normal middle ear structures in mutants (J). Sagittal histological sections of E10.5 control (L), Foxg1-Cre (M) and Pax2-Cre (N) mutant embryos. Early OV development is normal in both sets of mutant embryos, but the structure is slightly hypoplastic by E10.5 (M and N). The CVG is also enlarged in both Foxg1-Cre (M) and Pax2-Cre (N) mutants, when compared with a control embryo (L). CO, cochlea, SC, semicircular canals, P, pinna, O, ossicles (middle ear), Control, Tbx1+/−, Foxg1-Cre KO, Tbx1 null/flox; Foxg1-Cre/+, Pax2-Cre KO, Tbx1 null/flox; Pax2-Cre tg.
