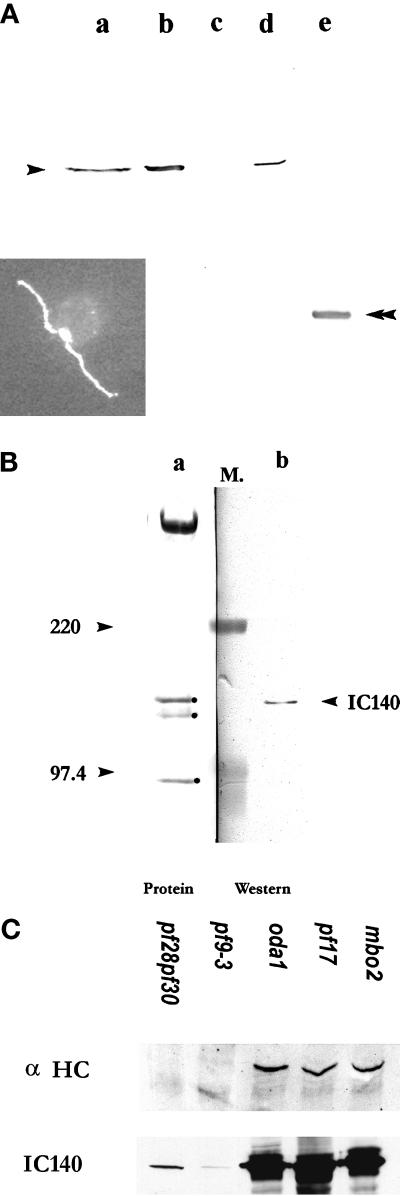
Figure 6.
Polyclonal antibody raised against the 53-kDa fusion protein of IC140 specifically recognized IC140. Western blots for Figure 6, A and B, were probed with the anti-IC140 serum followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibody and colorimetric development. (A) Lane a, wild-type high-salt extract; lane b, pf28 axonemes; lane c, pf28pf30 axonemes; lane d, I1 fraction from sucrose gradient of pf17 dynein extract; lane e, 53-kDa fusion protein. Inset, immunofluorecent microscopy illustrating that IC140 is located along both flagellar axonemes in wild-type Chlamydomonas cells. (B) Lane a, Amido Black staining revealing the proteins of the I1 fraction frompf28 axonemes including 3 ICs: 140, 138, and 97 kDa (dot); lane b, corresponding Western blot of the same 21S fraction. Molecular weight markers (M.) between lanes a and b were used for alignment. (C) Western blots and protein stains of overloaded gels revealed that IC140 is present in minor but detectable quantity in axonemes from pf28pf30 and pf9-3. For comparison, axonemes from control strains oda1, pf17, and mbo2 bear wild-type amounts of IC140. Axonemes (50 μg/lane) were separated in SDS-PAGE (4.5% for α HC, 7% for IC140 and Tubulin). Top panel, Western blot probed with affinity-purified anti-α HC (Myster, et al., 1997). Middle panel, Western blot probed with anti-IC140 serum. Bottom panel, tubulin (25 μg/lane) was revealed by Amido Black staining, showing equal loading of samples.