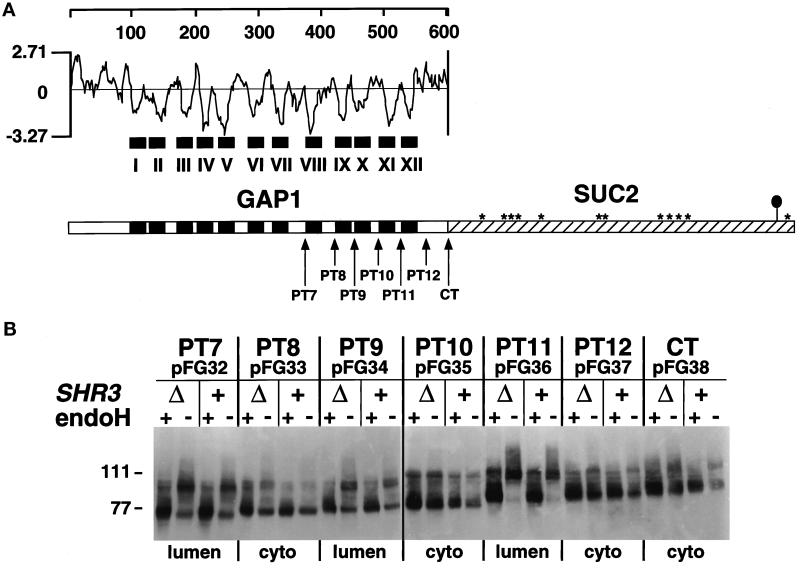
Figure 1.
Membrane topology of Gap1p in SHR3 and shr3Δ6 strains. (A) Hydrophilicity plot of Gap1p calculated according to the method of Kyte and Doolittle (1982) (window size of 11). The black boxes depict the 12 hydrophobic putative membrane-spanning domains (I–XII) present in Gap1p. In the schematic representation of the CT Gap1–Suc2p fusion protein, the white box represents Gap1p, and the hatched box represents the Suc2p reporter construct. Asterisks indicate potential glycosylation sites present within Suc2p. The black oval symbol in the C-terminal portion of Suc2p indicates the location of the HA3 epitope-tag. The arrows depict the locations of the junctions of the six (PT7–PT12) Gap1–Suc2p fusion proteins. (B) GAP1-SUC2 gene fusions (pFG32–pFG38) expressed in FGY84 (SHR3) and FGY85 (shr3Δ6). Transformants were grown in SUD (plus lysine and adenine), and extracts of total cell protein were prepared. Protein preparations were solubilized in SDS-PAGE sample buffer, treated with endoH where indicated, and resolved by SDS-PAGE in 7.5% polyacrylamide gels, immunoblotted, and analyzed as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The topological orientation of each Suc2p reporter and the positions of the molecular mass markers in kilodaltons are indicated.