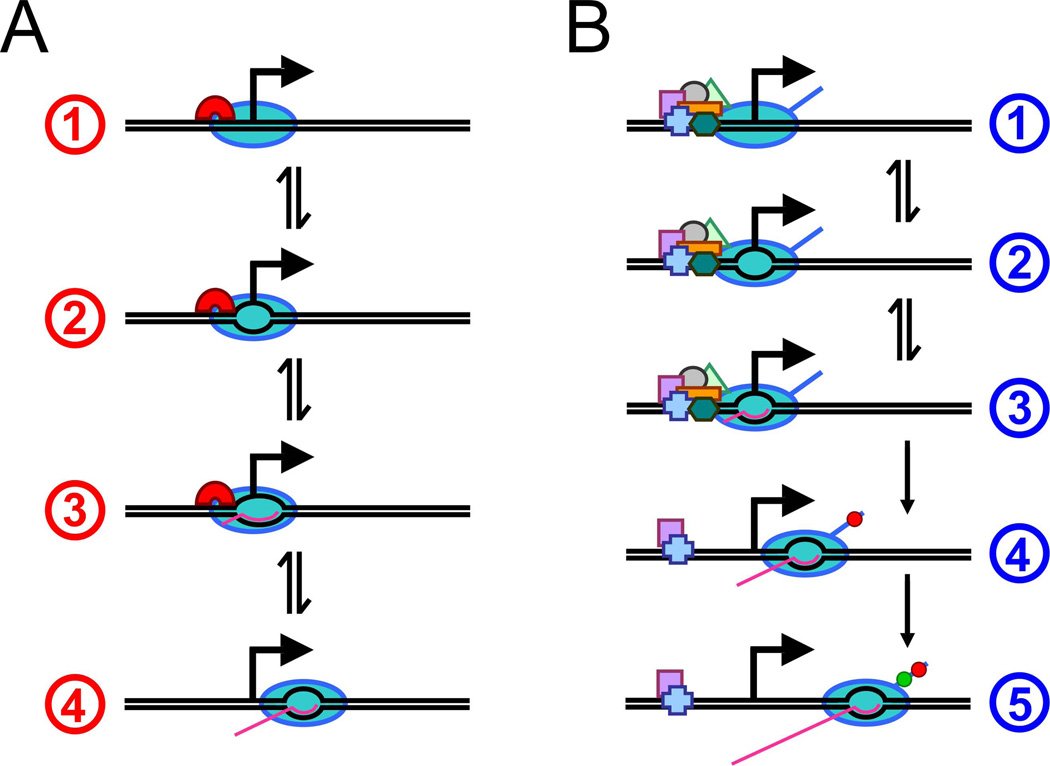
Figure 1. Steps in transcription initiation.
- Preinitiation closed complex formation at the promoter by RNAP holoenzyme (containing a σ factor).
- DNA is unwound around the transcription start site to form an open complex.
- Abortive synthesis of 2–15 nt RNAs requiring DNA “scrunching”.
- Promoter escape is typically associated with loss of σ factor.
- Preinitiation complex formation at the promoter with Pol II and general transcription factors.
- DNA is unwound around the transcription start site to form an open complex.
- Abortive synthesis of 2–3 nt RNAs.
- Promoter escape is associated with release of most general transcription factors and with phosphorylation at Serine 5 of the C-terminal domain of the largest Pol II subunit (red circle). In some eukaryotes Pol II pauses after synthesis of 20–50 nt RNAs.
- Escape from promoter-proximal pauses is associated with phosphorylation at Serine 2 of the C-terminal domain of the largest Pol II subunit (green circle) by pTEFb.