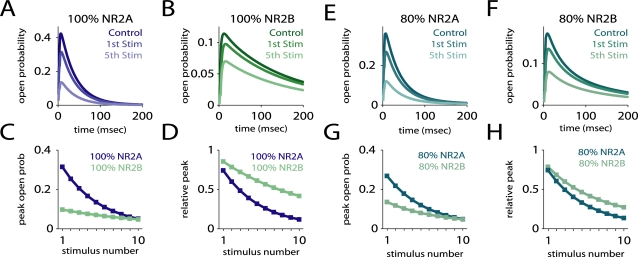
Figure 3. Estimating open probability using MK-801 block.
Simulation of an experiment that used brief pulses of glutamate and MK-801 to estimate the open probability of receptors given different NR2A/NR2B ratios [19]. The average behavior of NR2A and NR2B-containing receptors under this protocol was simulated using a probabilistic model. (A,B) The responses of NR2A and NR2B-containing receptors alone, showing the responses to glutamate alone (Control) and to the 1st and 5th stimulations. (C,D) The peak open probability upon successive stimulations, unnormalized (C) and normalized relative to the response to glutamate alone (D), showing that NR2A-containing receptors had a higher open probability, and were blocked more rapidly. (E–H) Same as above, but for two mixed populations of receptors. A population containing 80 percent NR2A-containing receptors had a higher open probability and was blocked more rapidly than a population containing 80 percent NR2B-containing receptors. However, when plotted relative to control (H), the block appeared very similar in the two cases. Similar results were observed for other mixed populations.