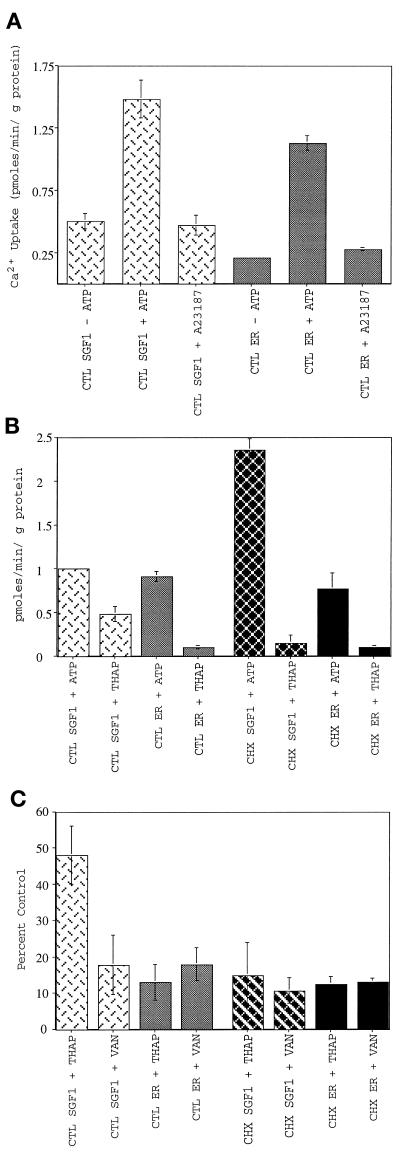
Figure 7.
Characterization of calcium uptake into SGF1s. SGF1 takes up calcium into a membrane-bound compartment in an ATP-dependent manner and is blocked by known inhibitors of SERCA and all p-type ATPases. CTL SGF1 (light cross-hatched bars), CTL ER (light solid bars), CHX SGF1 (dark cross-hatched bars), and CHX ER (dark solid bars) are indicated. (A) ATP-dependent calcium uptake into CTL SGF1 and CTL ER fraction. Calcium uptake in pmoles per minute per microgram of protein is plotted. Uptake reactions were performed in the presence of 75 nM free calcium by using 25 μg of SGF1 or 100 μg of ER for 10 min at 37°C in the absence of ATP, in the presence of 1 mM ATP, or in the presence of 1 mM ATP and 1 μM A23187. The 10-min time point was within the linear range of calcium uptake (see Figure 11). Note that background (uptake in the absence of ATP) is not subtracted from any of these experiments. (B) Thapsigargin sensitivity of calcium uptake into CTL and CHX SGF1s and CTL and CHX ER fractions. ATP-dependent calcium uptake in pmoles per minute per microgram of protein (after background subtraction from a minus ATP reaction) is plotted for all four fractions. Thapsigargin (2 μM) was added to the reaction mixture containing 1 mM ATP at 4°C for 5 min before initation of the assay by rapid warming to 37°C. (C) Inhibition of calcium uptake by thapsigargin and sodium vanadate. Calcium uptake is expressed as percent of CTL (no inhibitor) for all four fractions. Thapsigargin (2 μM) was added to the reaction mixture at 4°C for 5 min before initation of the assay by rapid warming to 37°C. The fractions were pretreated with 1 mM sodium vanadate for 10 min at room temperature in the absence of ATP before warming to 37°C and addition of ATP. Error bars represent SD, and n = 25 for A, and n = 6 for B and C.