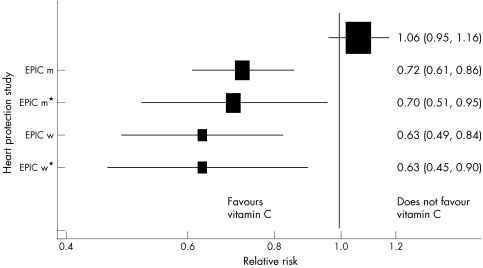
Figure 2 Estimates of the effects of an increase of 15.7 μmol/l plasma vitamin C on CHD five year mortality estimated from the observational epidemiological EPIC study and the randomised controlled heart protection study. EPIC m, men, age adjusted; EPIC m*, men, adjusted for age, systolic blood pressure, cholesterol, BMI, smoking, diabetes, and vitamin supplement use; EPIC f , women, age adjusted; EPIC f*, women, adjusted for age, systolic blood pressure, cholesterol, BMI, smoking, diabetes, and vitamin supplement

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.