Fig. 1.
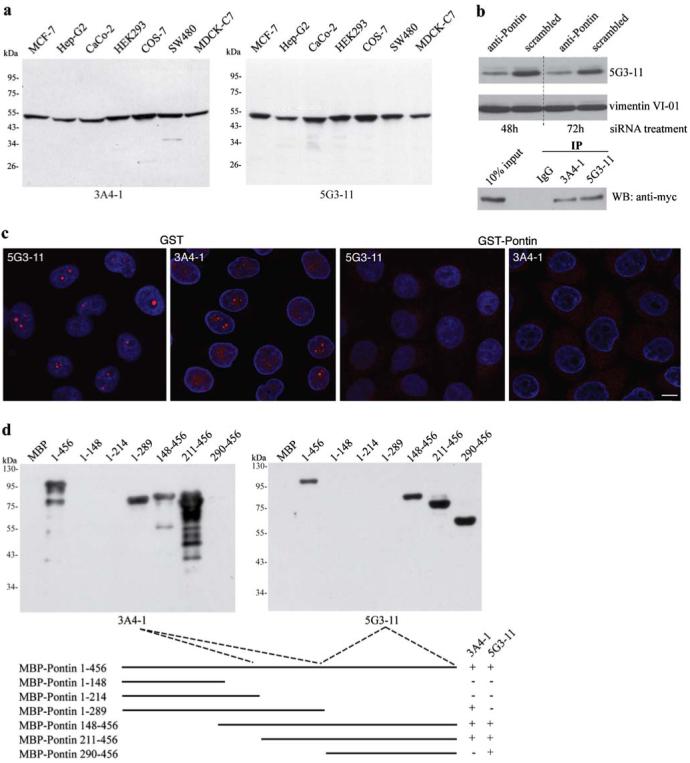
Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Pontin. a Monoclonal antibodies were raised against the full-length recombinant protein and their specificity tested on whole-cell extracts from different cell lines. Only one band of an apparent molecular weight of 50 kD is detected by either one of the antibodies. b To further confirm the antibody specificity, Pontin was detected by the anti-Pontin (5G3-11) antibody in extracts made from cells treated for 48 h or 72 h with anti-Pontin siRNA. A ∼50% reduction at the protein level was observed after the siRNA treatment. In addition, both anti-Pontin antibodies specifically immunoprecipitated Myc-tagged Pontin from cell extracts. c Immunofluorescence labeling of HeLa cells with mouse anti-Pontin monoclonal antibodies (red). DNA counter-stained with DAPI (blue). Prominent dots within the nucleolus were observed in a subset of cells. Staining in the nucleus disappeared after pre-incubation of antibodies with GST-Pontin but not with GST alone showing the specificity of the staining. Scale bar represents 10 μm. d Different regions of Pontin were expressed in E. coli as MBP fusion proteins, purified and used for epitope mapping. The anti-Pontin (3A4-1) antibody interacts with an epitope between the Walker A and B motifs of the protein (amino acids 214-289) while anti-Pontin (5G3-11) antibody binds to an epitope within the C-terminal amino acids 290-456
