Fig. 5.
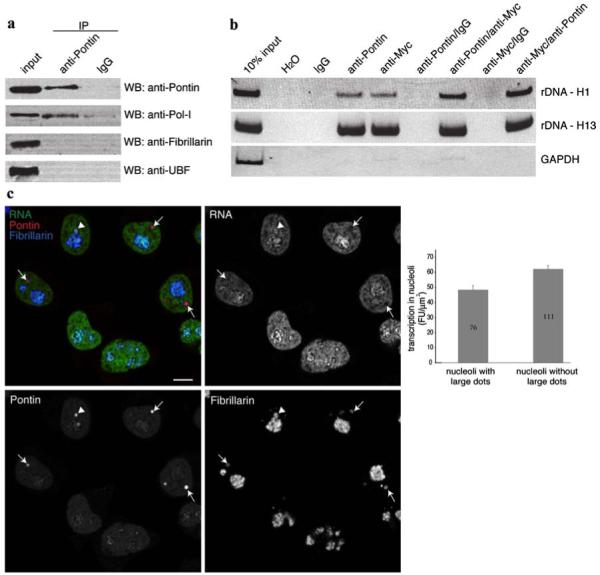
Pontin is involved in the regulation of rRNA transcription. a Pontin was immunoprecipitated using the anti-Pontin (3A4-1) antibody and nuclear proteins detected by immunoblotting. Pol I was specifically precipitated with anti-Pontin antibody but not with a control antibody. b rDNA loci H1 close to the transcription initiation site (952-1,030 bp) and H13 close to the termination site (12,855-12,970 bp) were enriched after chromatin immunoprecipitation with anti-Pontin (5G3-11) or anti-Myc antibodies. Moreover, both regions were specifically amplified after two-step immunoprecipitation with anti-Pontin/anti-Myc or anti-Myc/anti-Pontin antibodies but not with control IgG antibodies showing that Pontin and c-Myc binds to the same regions of rDNA in a complex. Constitutively active GAPDH promoter served as a negative control. c Transcriptional activity of nucleoli containing large Pontin dots is reduced. Newly synthesized RNA (green) was labeled by 10 min incubation with 5-fluorouridine and visualized together with Pontin (red) and fibrillarin (blue) as a marker of nucleoli. In transcriptionally active nucleoli, rRNA signal surrounded Pontin labelling (arrowhead). However, most nucleoli that contained Pontin dots exhibited reduce transcription activity (arrows). Quantification of nucleolar transcription (fibrillarin signal was used as a mask) revealed that transcription activity was reduced by ∼20% in nucleoli where Pontin is sequestered in large dots (average nucleolar fluorescence of transcription signal with standard error of the mean is shown together with number of nucleoli analyzed)
