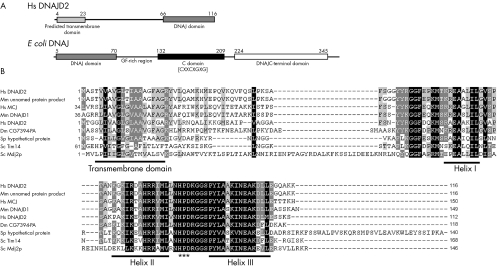
Figure 4 DNAJC19 has an unusual domain architecture with respect to other DNAJ proteins and similar proteins are found in various species. (A) Graphical representation of the domain structure of H sapiens DNAJC19 v the E coli DNAJ/HSP40 protein. The DNAJC19 protein contains only the DNAJ domain (pfam00226.11), which is located at the C‐terminus following a predicted transmembrane domain. This is in contrast with the E coli DNAJ/HSP40 protein which is the classical example of a DNAJ protein. The DNAJ domain (pfam00226.11) is located at the N‐terminus of the protein followed by a glycine/phenylalanine‐rich linker domain, a cysteine‐rich domain (pfam00684.11) containing four copies of a zinc‐finger‐like motif (CXXCXGXG), and a C‐terminal domain (pfam01556.11) of unknown function. (B) ClustalW multiple sequence alignment of DNAJC19 homologues (see Electronic‐Database Information section for GenBank identification numbers). The conserved helix structures of the DNAJ domain are underlined; the DNAJ domains of these proteins only contain three of the helices that make up the classical tetrahelical DNAJ domain. They all also contain the absolutely conserved HPD motif which is indicated by (***). Highlighted regions indicate conserved blocks of sequence. Residues highlighted in black indicate positions with highest degree of conservation and those highlighted in grey indicate less highly conserved positions. Gaps introduced to optimise the alignment are indicated by dashes (–). Alignment was adjusted in Genedoc based on previously published alignments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.